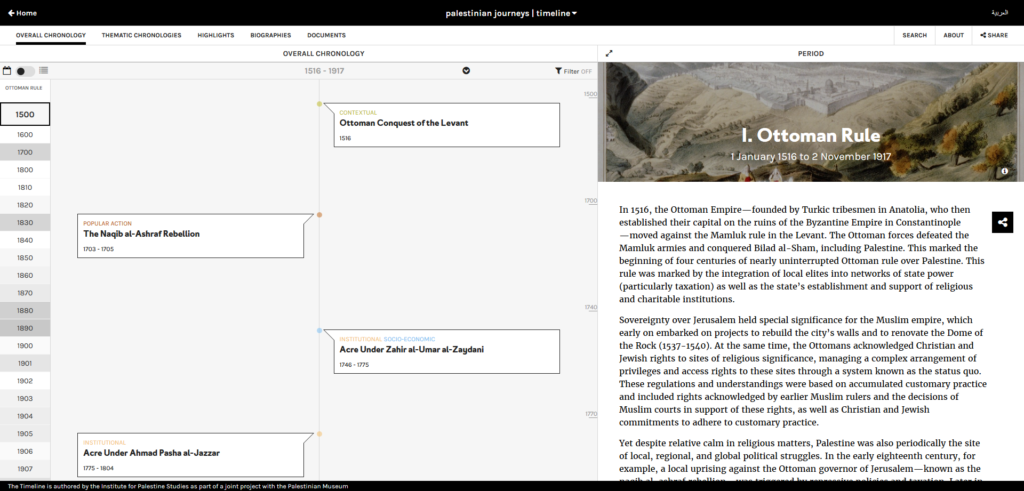
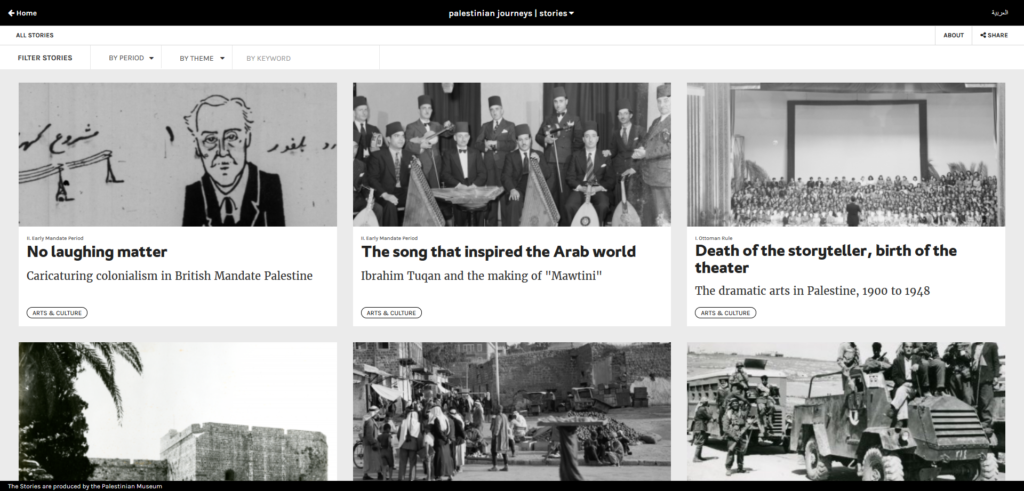
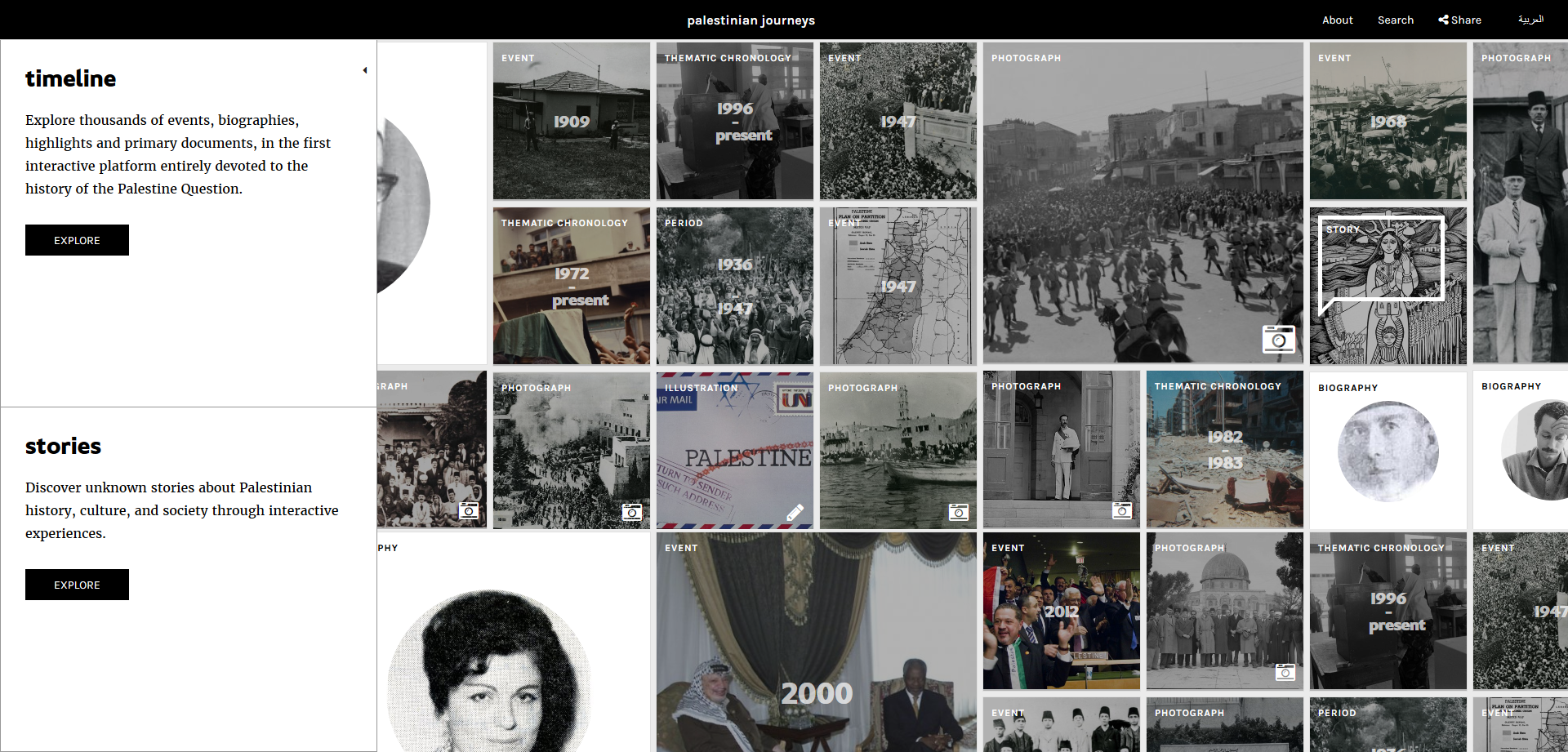
Launched in 2007 as a “citizen media platform”, 7iber became in 2009 a registered LLC (Limited Liability Company) in Jordan and grew into both a media organization and an online magazine. Over the years, 7iber received grants and funding from the European Endowment for Democracy (EED), The Netherlands Embassy in Amman, International Media Support (IMS), the Swiss Embassy in Amman, Hivos, the Open Society Foundation, Heinrich Boell Foundation, the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA), InterNews, and the Arab Partnership Participation Fund.
7iber advocates for “an open society that upholds values of accountability, rule of law, human rights, and pluralism, through in-depth multimedia journalism, critical analysis and public conversation.” To do so, they produce and publish original articles, provide a platform for public debate, organize talks, conduct “research on Internet governance and digital rights”, and offer training opportunities “on various aspects of online media.”
Excerpt from the “About” page, December 13, 2012.
Navigate 7iber
Content on 7iber can be discovered via the categories listed below:
-
- Politics and economics / سياسة واقتصاد
- Arts and culture / ثقافة وفنون
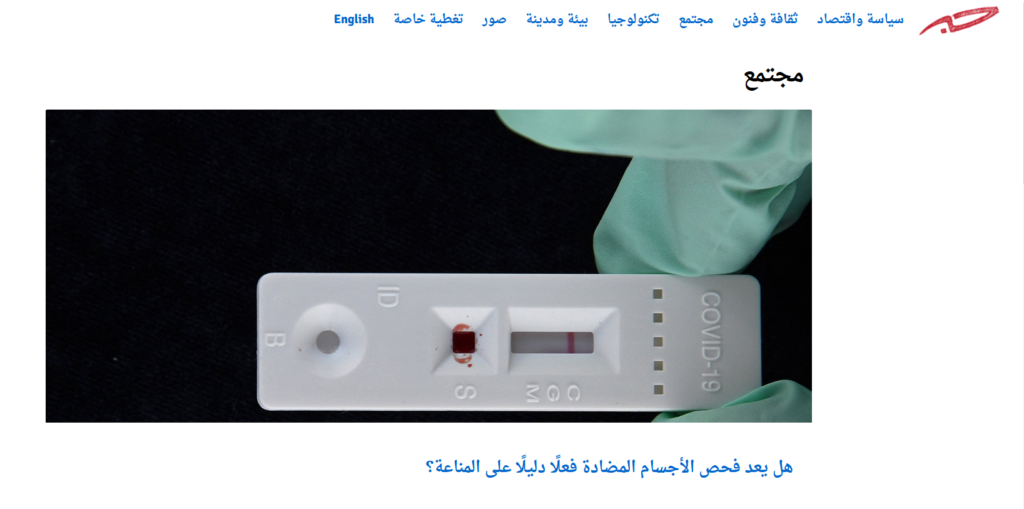
- Society / مجتمع
- Technology / تكنولوجيا
- Environment and urban issues / بيئة وقضايا المدينة
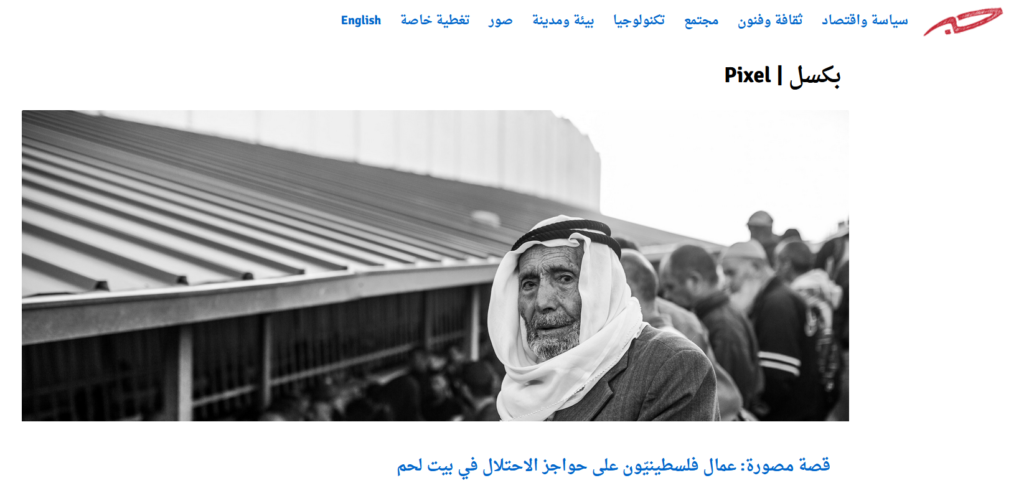
- Images / صور
- Special coverage / تغطية خاصة.
7iber on Social Media
In sum
7iber produces and publishes original news content that will be interesting to anyone looking for un-official information, especially related to Human Rights or political pluralism in the Arab World. As would be the case on any online media platform, it is recommended to cross-check 7iber information and data with those published elsewhere.
The interface is available in Arabic only but some articles are accessible in English.