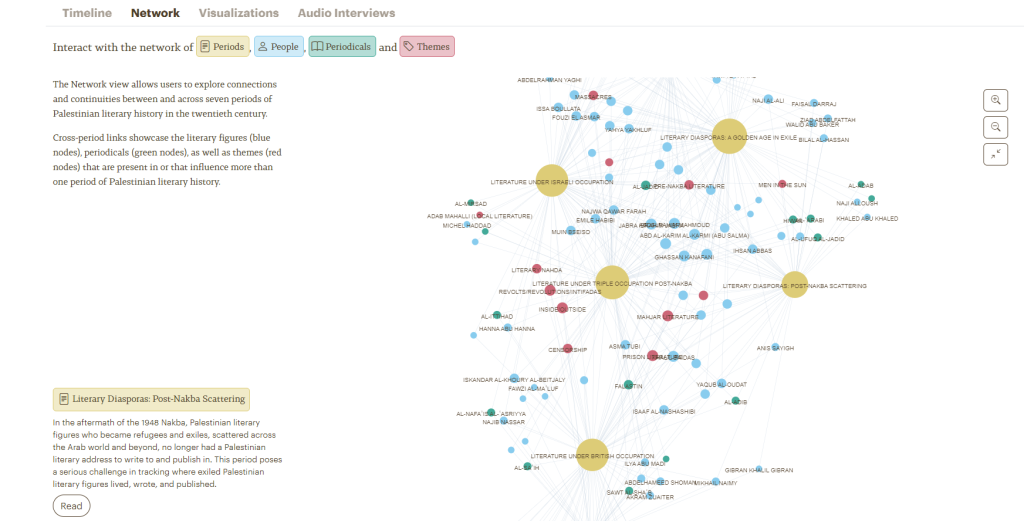
The South Asia Open Archives (SAOA) is a collaborative effort spearheaded by the Center for Research Libraries to increase the availability in Open Access of materials useful for the study of South Asia. SAOA is a subset of CRL’s South Asia Materials Project (SAMP), aiming “at addressing the current scarcity of digital resources pertinent to South Asian studies and at making collections more widely accessible both to North American scholars and to researchers worldwide.”
Supported by members contributions, SAOA focuses primarily on colonial-era documents that have value to research, potential for a wide audience, are rare and in need of preservation, and complement existing resources. Thanks to a partnership with JSTOR the collection is accessible via their platform, benefiting from “the advanced functionalities and user-friendly features” they developed.
The South Asia Open Archives offers over one million pages of content (approximately 50,000 items) and is made of two collections: the Print collection and the Manuscripts collection.
PRINT Collection
The South Asia Open Archives (SAOA) | Print collection contains over 30,000 digitized print items including periodicals (newspapers, serials, journals), archival materials (colonial reports, censuses, government documents), other publications (arts, history, literature, economics, politics, etc.) and reference works (encyclopedias and dictionaries).

Spanning from the late-18th to the 21st century, the SAOA | Print collection is a rich and continually growing collection of digitized primary sources made available in Open Access to worldwide scholars, students, and researchers.
MANUSCRIPTS Collection
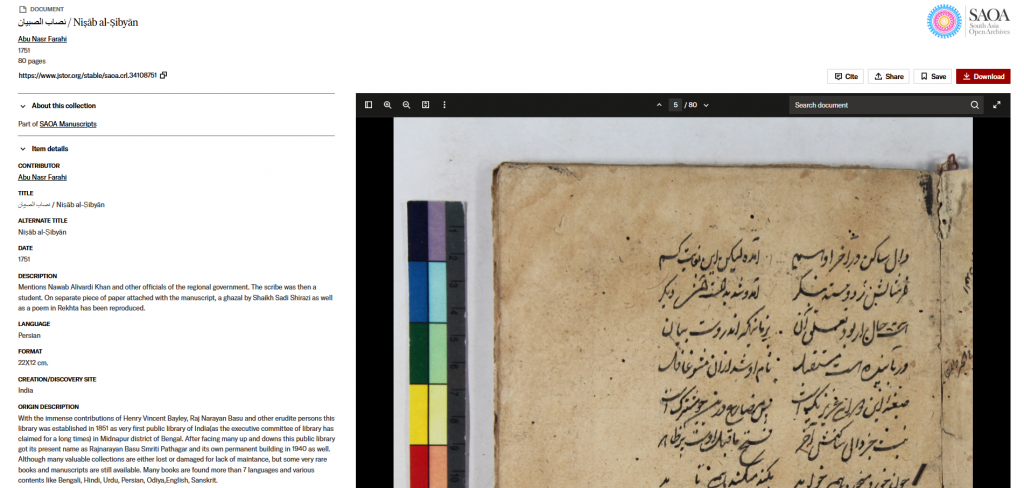
The South Asia Open Archives (SAOA) | Manuscripts collection is a pilot project that only included 13 items at the time of our visit. However, one can hope that the collection will grow overtime.
In both collections, documents can be opened in the online reader, shared (stable URL), saved to your JSTOR library, or downloaded in PDF.
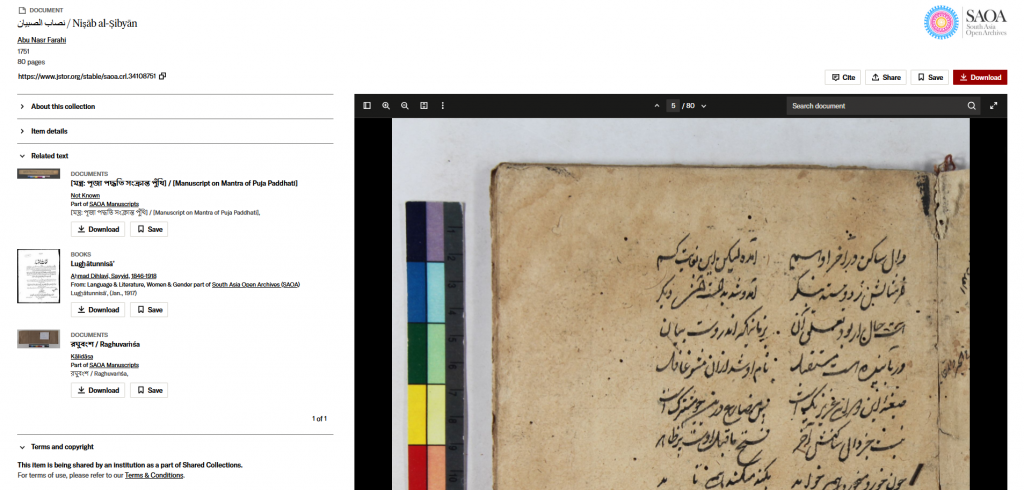
In addition to detailed information on the item, the reader also suggests related texts (see below) allowing the user to navigate through the collection.
All documents in the collection are subjected to JSTOR Terms & Conditions of use. To learn more about the South Asia Open Archives, a Statement of Value is available for consultation.