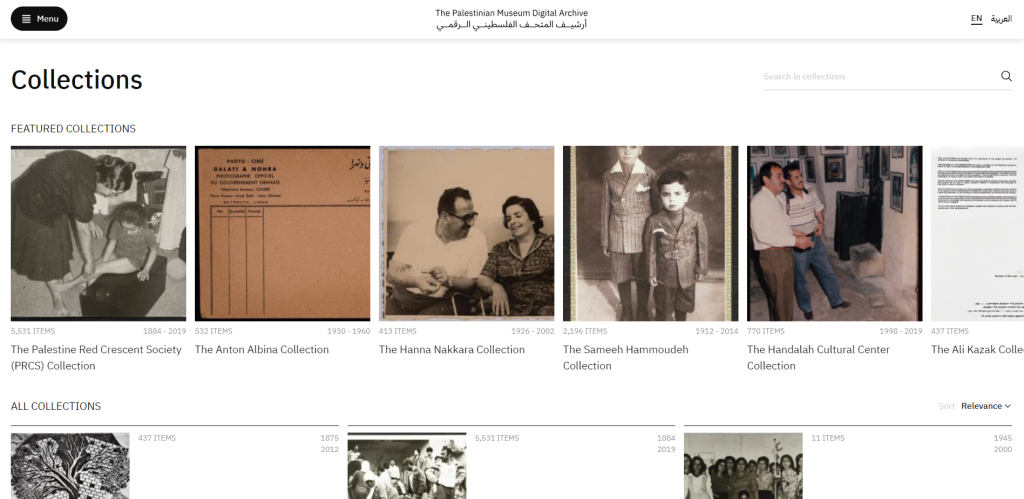
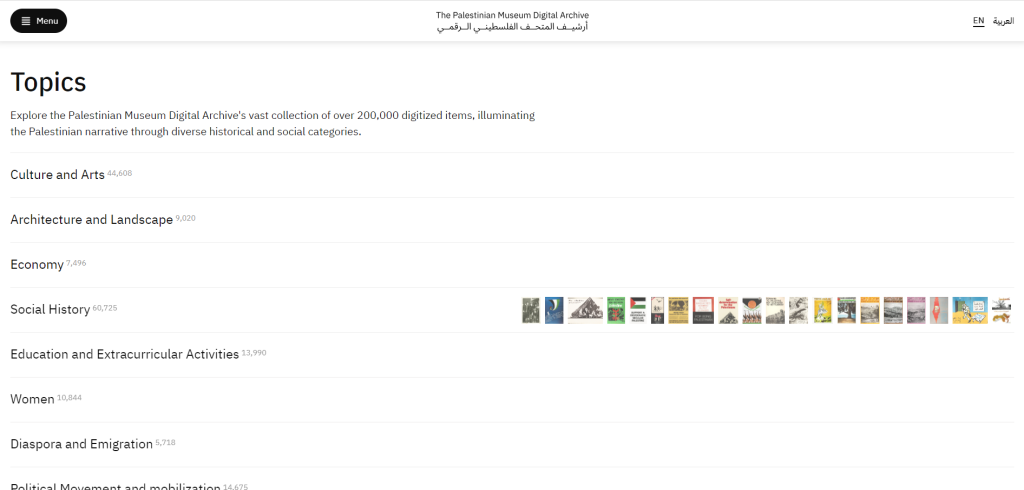
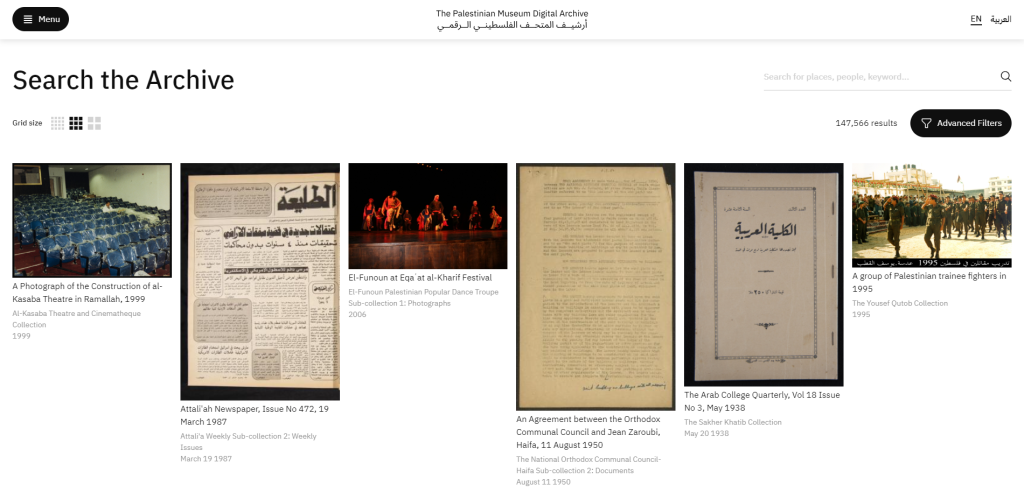
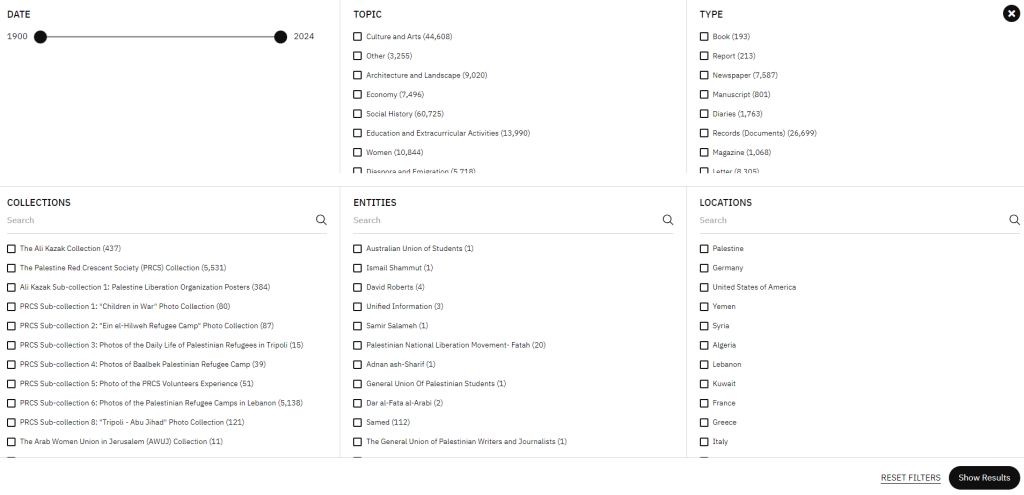
Middle East Women’s Activism (MEWA) is a digital collection of the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS) Library that includes the recordings of audio interviews conducted in 2013 and 2014 by Nicola Christine Pratt, a Politics and International Studies Professor at the University of Warwick. These interviews served as the basis of a publication entitled Embodying Geopolitics: Generations of Women’s Activism in Egypt, Jordan and Lebanon. A complete description of professor Pratt’s research project and field trip can be found on the ‘About‘ page. The full list of interviews (94 in total) is available through SOAS Library catalogue:
Depending on the age of the individual, narratives include details about women’s contributions to the early years of post-independence state building, the impact of the 1967 Arab-Israeli war, women’s participation in revolutionary and radical movements in the 1970s, including the Palestinian National Movement, women’s roles in the Lebanese Civil War of 1975-1990, the rise of NGOs and women’s involvement in the 2011 uprisings.
https://digital.soas.ac.uk/mewa/about/
At the time of our visit, MEWA only included fifteen interviews -mostly in Arabic- with Egyptian, Jordanian and Lebanese women activists from different generations. One can assume that more interviews will be added overtime. Ranging from 30 minutes to one hour in length, the recordings can be listened to directly from the digital collections platform:

In addition to the audio recordings, English transcripts (when interview was conducted in English) or English translations (when interview was conducted in Arabic) are available in different formats. Visitors can move from one view to another using the tabs menu at the top of the page.



Another interesting feature included in MEWA is the option to visualize the exact location where the interview was conducted:


Each interview is thoroughly described in a variety of standardized formats making it easy for anyone who would want to reuse it:




It is also possible to download all items related to an interview from the same page. Downloads include:
- the description in word (docx)
- the transcript in pdf
- the audio recording in mp3, ogg and wav.

Last, visitors can access usage statistics of each interview published on MEWA:

This digital audio archive will appeal not only to scholars but also members of the general public.