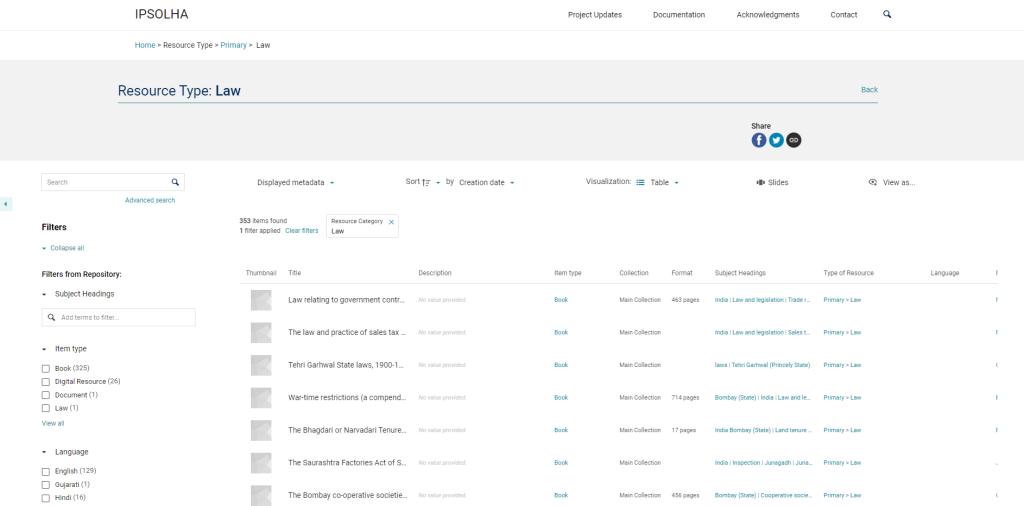
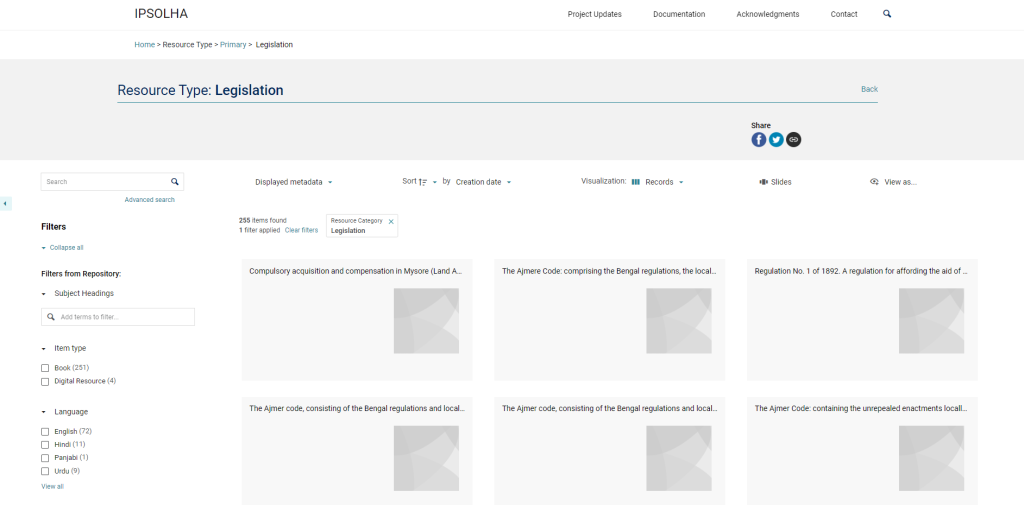
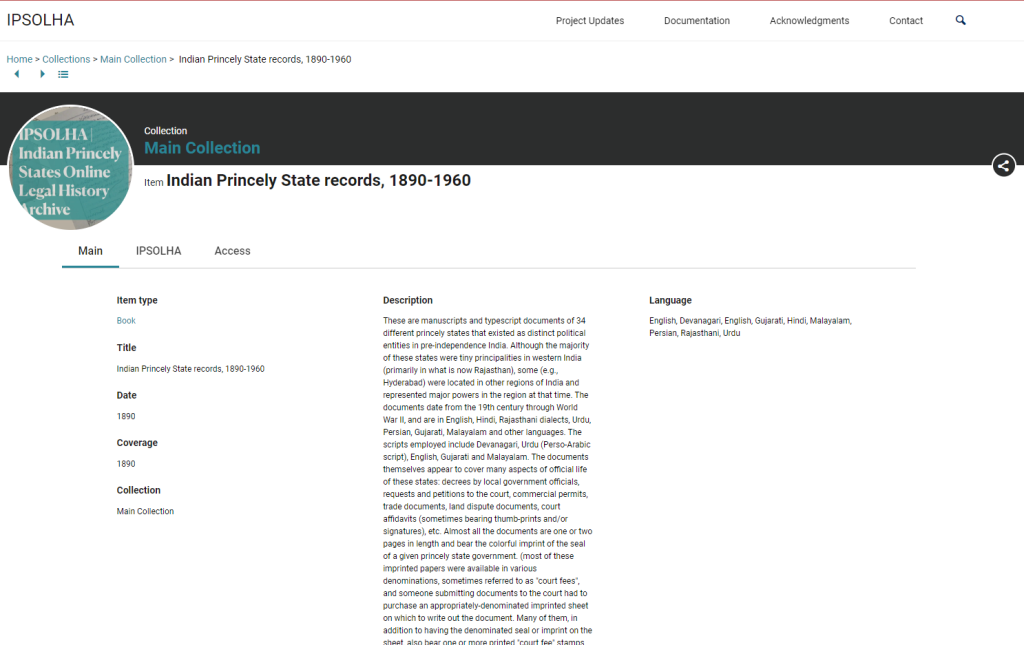
Launched in 2013, Corpus Musicae Ottomanicae (CMO) is a 12-years long project focusing on publishing critical editions of 19th century Near Eastern music manuscripts and more specifically Ottoman music manuscripts. CMO is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), and relies on the close collaboration of two main institutions:
- the Orient-Institut Istanbul handling all institutional relations in Istanbul, and project tasks such as cataloging, edition preparation, and sourcing
- the Max Weber Foundation in Bonn (German Institutes of Humanities Abroad) providing the technical infrastructure and support for digital publishing.
Other partners involved in the project include Istanbul University Research Institute of Turkology (İstanbul Üniversitesi Türkiyat Araştırmaları Enstitüsü), Istanbul Technical University Turkish Music Conservatory (İstanbul Teknik Üniversitesi Türk Musikisi Devlet Konservatuarı), Bilkent University Department of Turkish Literature (Bilkent Üniversitesi Türk Edebiyatı Bölümü).

“These sources are of prime importance both for musicological research and for the broader cultural history of the Ottoman Empire. They offer the opportunity to uncover forgotten repertoire, to shed new light on Ottoman sung poetry, and to contribute towards a diverse, multidisciplinary history of the urban culture of the region.“
https://www.uni-muenster.de/CMO-Edition/en/cmo/cmo.html
“Hampartsum” (or “Hamparsum”) notation
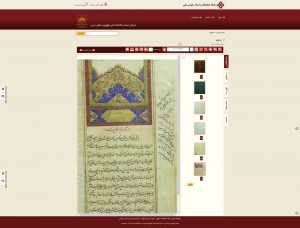
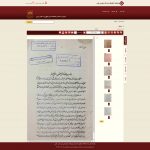
The main notation system used to record the music of Ottoman Istanbul as of the beginning of the 19th century, was developed by the Ottoman Armenian composer Hambarjum Limōnčean (Tr. Hamparsum Limonciyan, 1768–1839) and named after him: “Hampartsum” (or “Hamparsum”). “This notation system was well adapted to the modal and rhythmic principles of Ottoman music, and was used by both Armenian and Muslim–Turkish musicians throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries. If “Hampartsum” was the dominant system throughout the 19th century, the European staff notation system was also used as demonstrated by a large number of manuscripts written in both notation systems.
Corpus Musicae Ottomanicae aims to publish critical editions of manuscripts of Ottoman music written in Hampartsum notation as well as of manuscripts written in staff notation during the same period. The project will produce parallel editions of song texts found in manuscripts, and populate the comprehensive online source catalogue of printed and manuscript sources for Ottoman music to provide a major resource for researchers and performers.
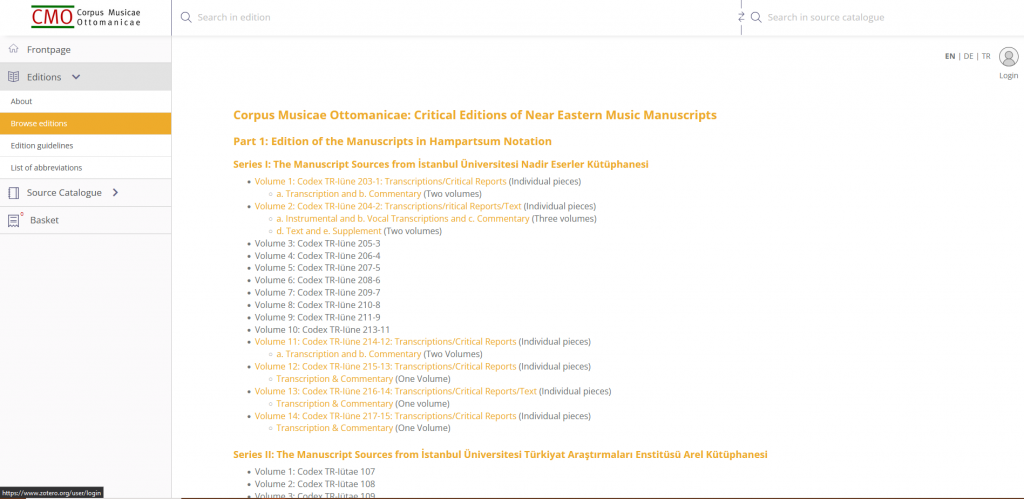
The critical Editions of music manuscripts section allows visitors to browse editions and access a list of abbreviations. Edition guidelines are expected to become available soon. The Source catalogue allows visitors to browse music pieces and song texts by source, Makâm (i.e. mode), Usûl (rythmic cycle), Genre and Incipit.
Corpus Musicae Ottomanicae also developed a number of guidelines and tools to facilitate the critical editions of Ottoman music manuscripts written in Hampartsum notation. Among those, we find Guidelines for the transcription of the Ottoman Lyrics from Arabic into Latin Characters, a list of Standard musical terms, Truetype fonts for Hampartsum-notation, and A note on terms and translitteration.
In 2017, CMO published the proceedings of an international conference on “Rythmic Cycles and Structures in the Art Music of the Middle East” held in 2014 at the University of Münster. The volume named after the conference can be purchased from the publisher.
Corpus Musicae Ottomanicae website is available in German, English and Turkish.