bina is the digital collection of the Bibliothèque Universitaire des Langues et Civilisations (BULAC), an academic library established in 2001 to centralize the “Oriental” collections of nine parisian academic and research libraries. The wide-range of geographical areas covered by BULAC go from the Balkans, to Oceania passing by the Middle East, Central Asia, Africa, and Asia. BULAC’s mission revolves around three axis: gathering these “Oriental” collections in a single location, promoting and supporting open access, and facilitating worldwide scholars’ access to the materials.
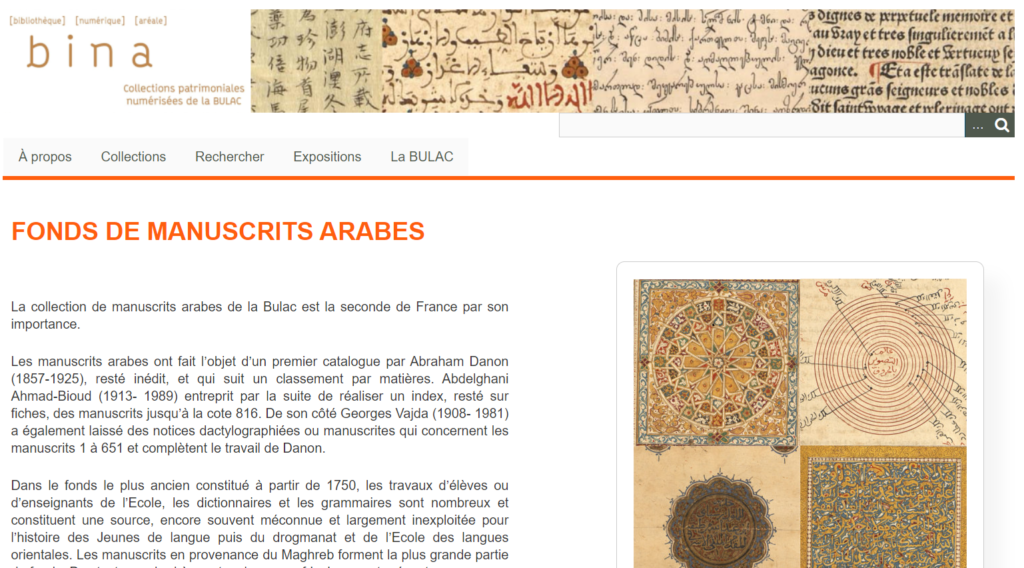
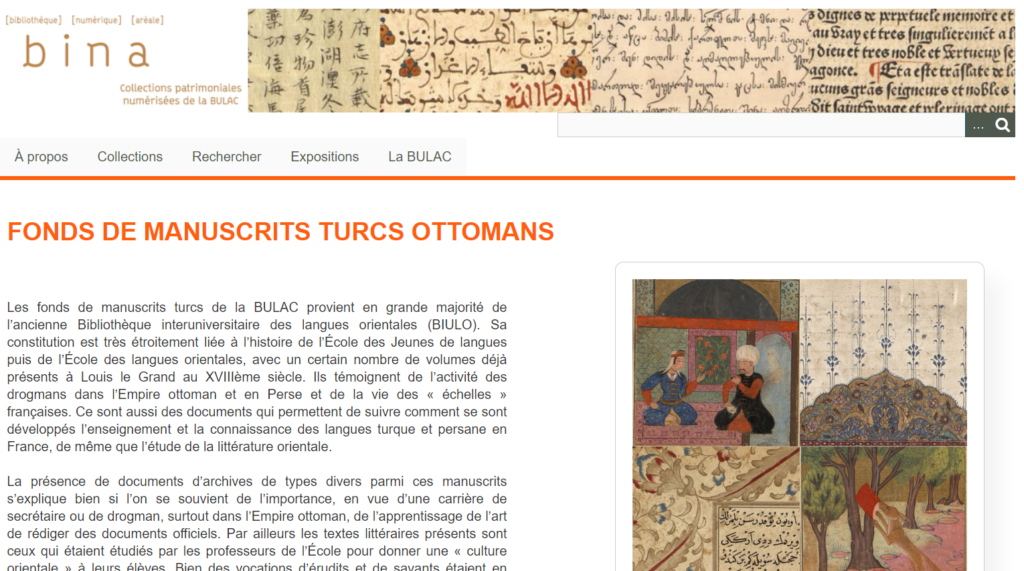
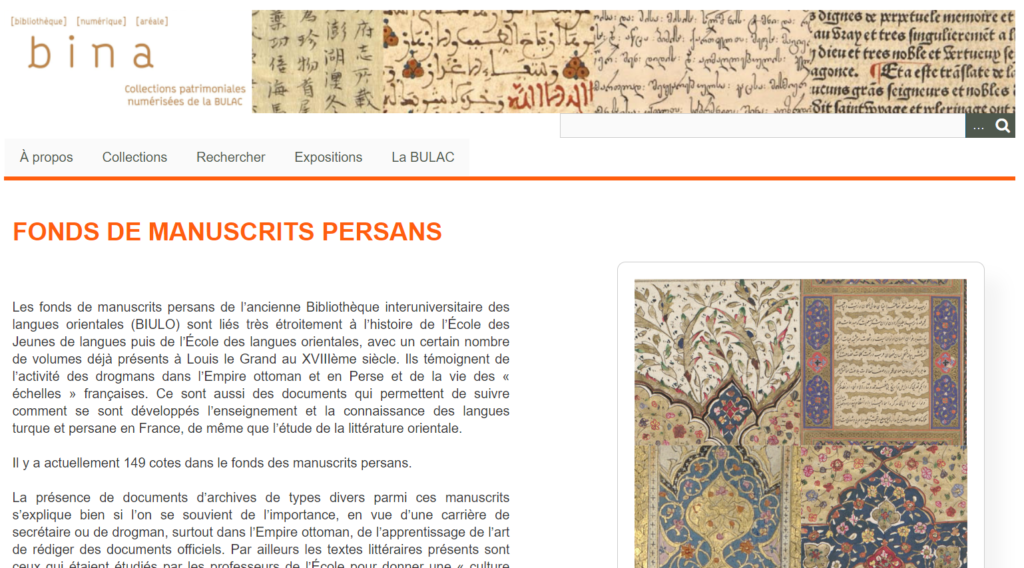
The Middle Eastern, North African and Central Asian collections of BULAC include 235,000 monographs and over 800 periodicals. In addition, the library owns approximately 4,000 “Oriental” manucripts and rare books dating from the 16th to the 19th century. The online cataloguing of these rare collections started in 2013 and the digitization in 2016. At the time of our visit (June 2021), 248 Ottoman Turkish, 150 Persian and 61 Arabic manuscripts and archival documents had been scanned and were available in bina.
The XML-EAD standard initally used to describe these rare materials was not fit to reflect the linguistic and paleographical variety of the collection and the multiple transliteration systems used to transcribe non-roman scripts. Therefore, BULAC worked in collaboration with the Agence bibliographique de l’enseignement supérieur (ABES) to develop bibliographic descriptions and authority records matching the codicological and onomastical specificities of these collections. Those interested in learning more about this cataloguing project can read the following articles (in French):
- « Les manuscrits arabes de la BULAC », 30 septembre 2013 : https://bulac.hypotheses.org/221
- « Les manuscrits turcs et persans de la BULAC », 29 novembre 2013 : https://bulac.hypotheses.org/333
- « Le signalement en ligne des manuscrits arabes, persans et turcs de la BULAC », 18 juillet 2016 : https://bulac.hypotheses.org/4890
Navigating bina digital collections can be done in three different ways. The simple search available from the top-right corner of the page will search simultaneaously the title, author, date, description, format and subject fields. The advanced search available either by clicking on the “Rechercher” tab or opening the drop-down menu in the simple search will allow to target specific fields and cross-search them. The Index search allows to browse materials by author, language, type of document and call number.
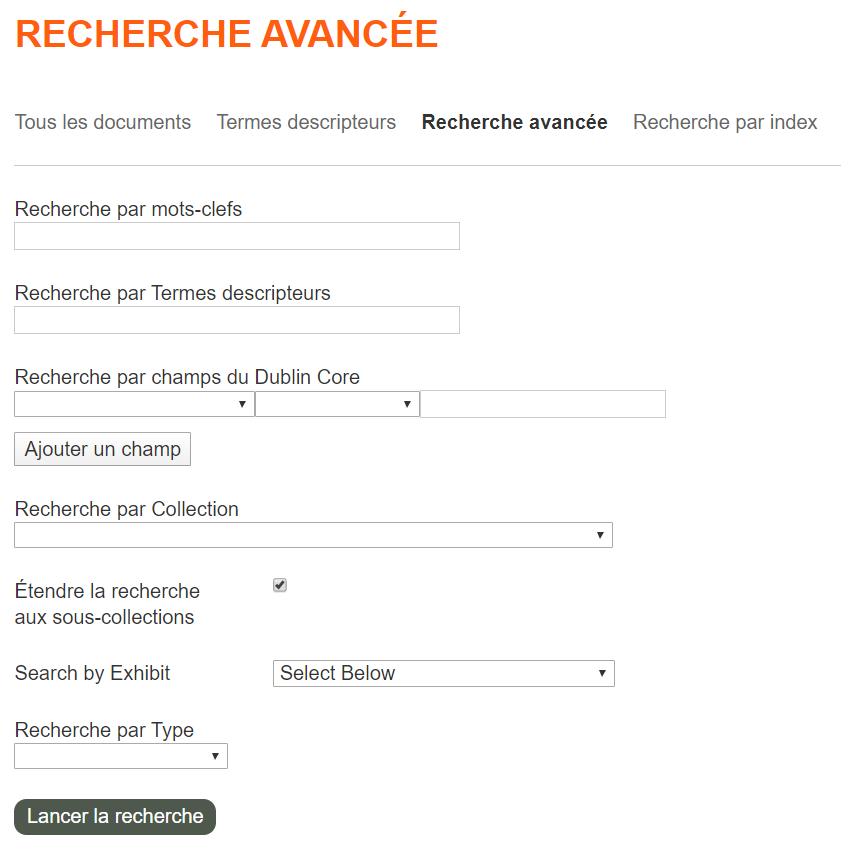
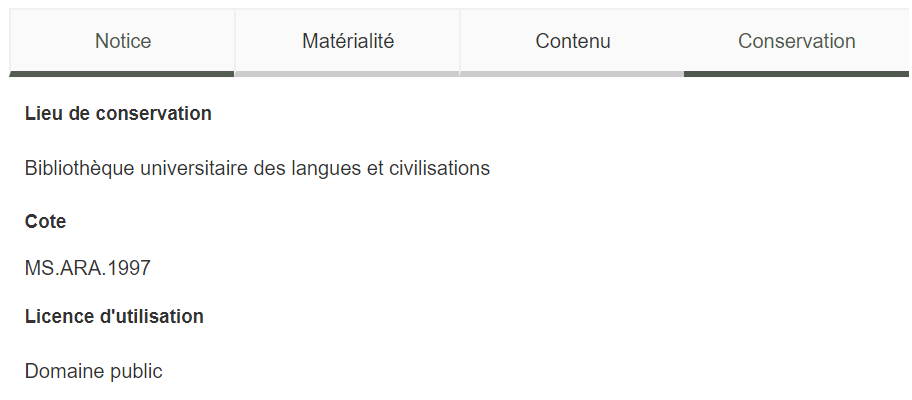
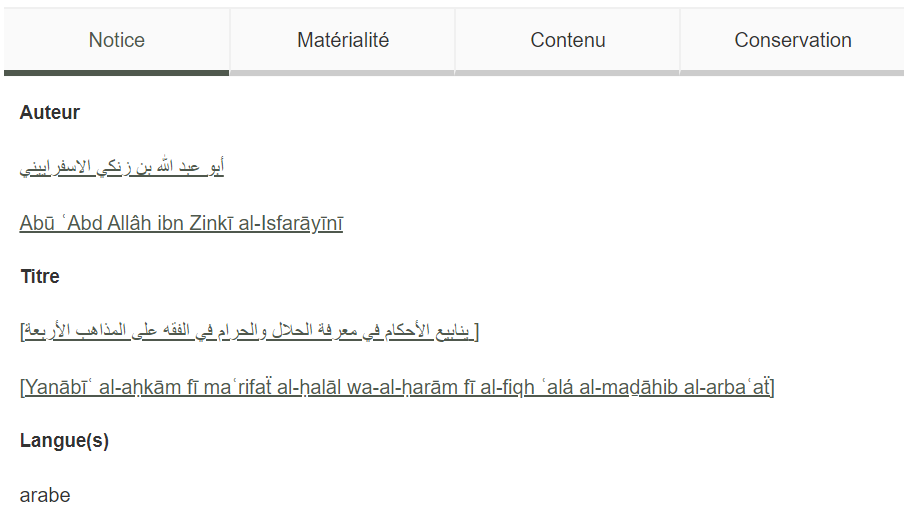
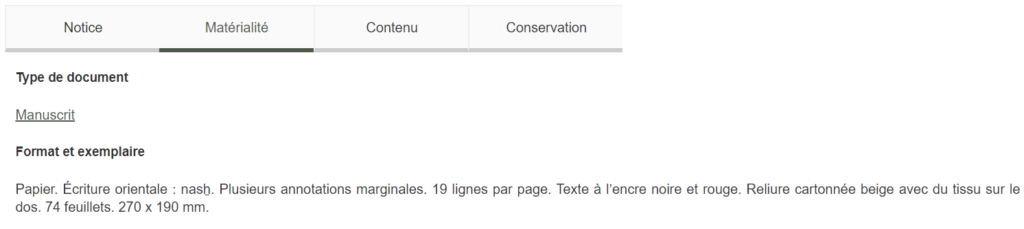
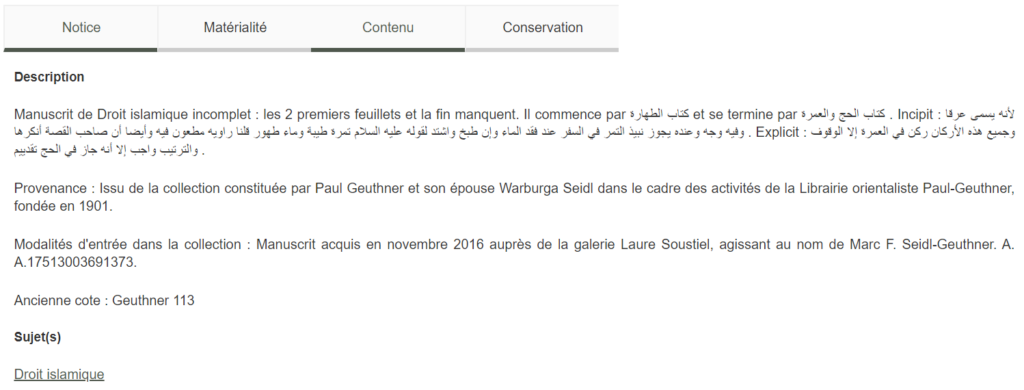
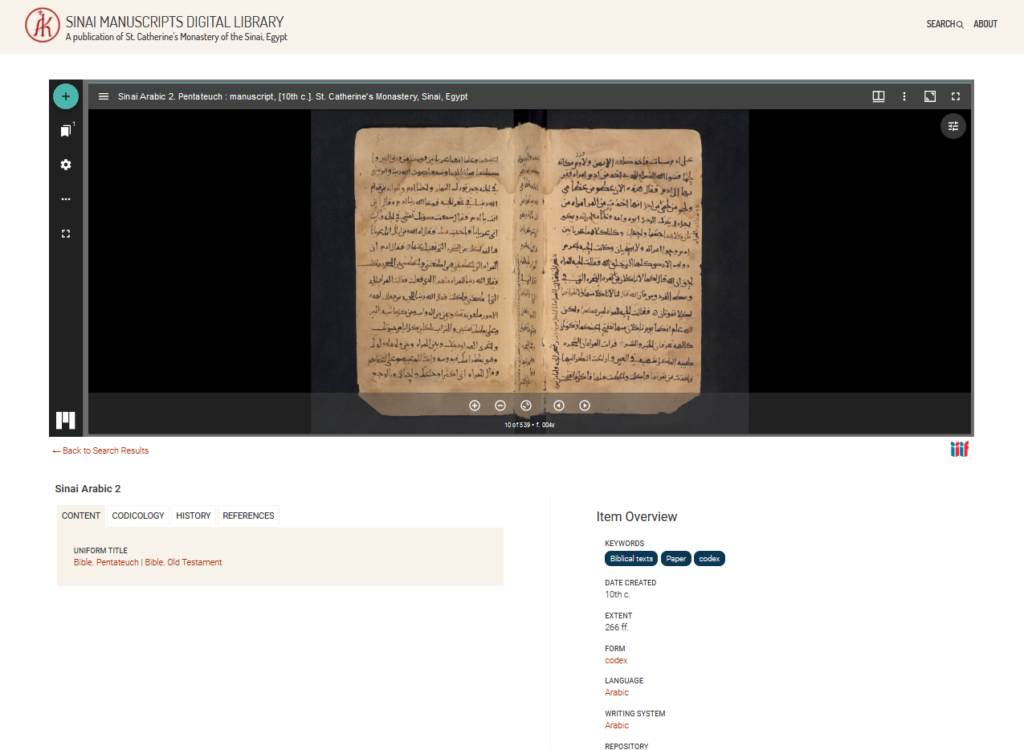
The metadata is divided in four categories: Notice (bibliographic data), Matérialité (physical description), Contenu (content) and Conservation (location).
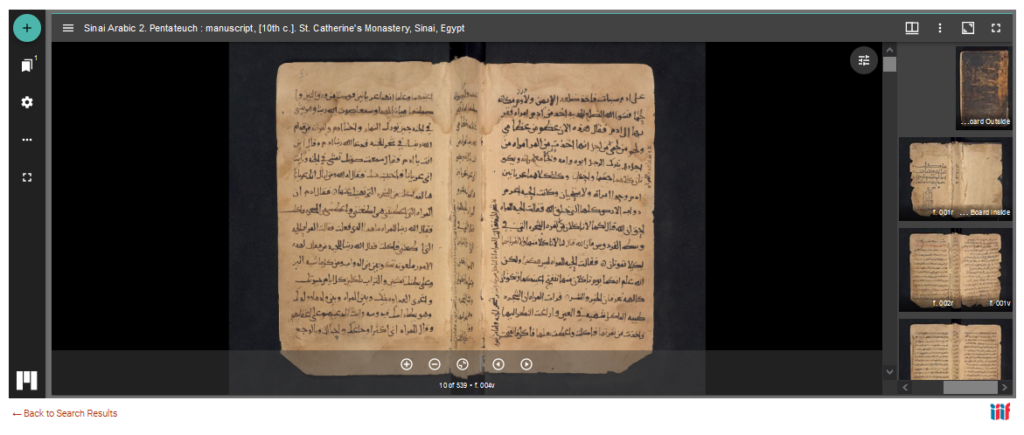
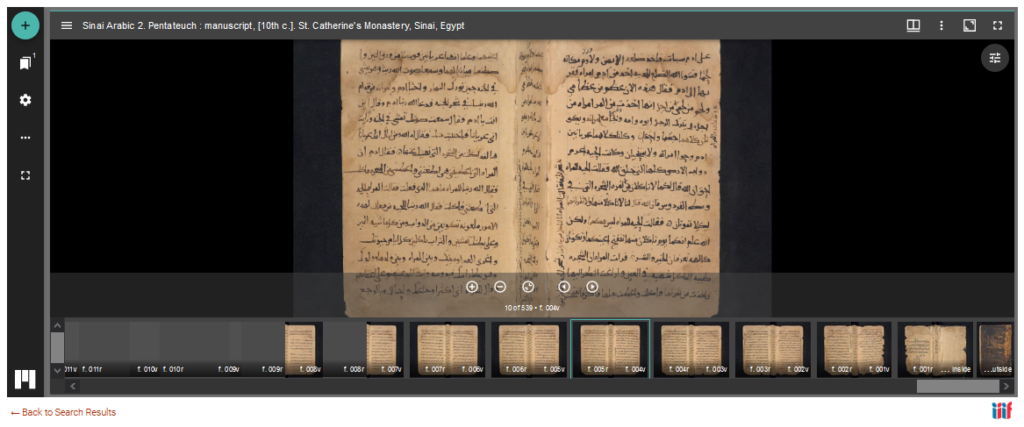
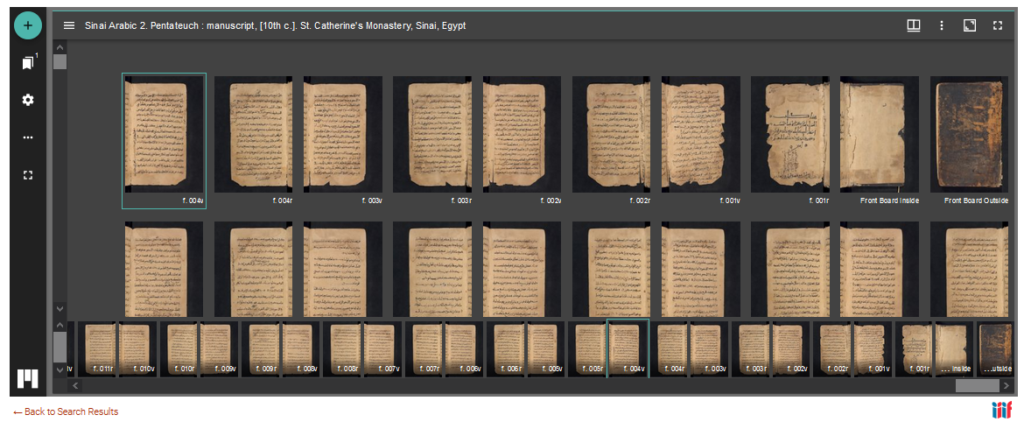
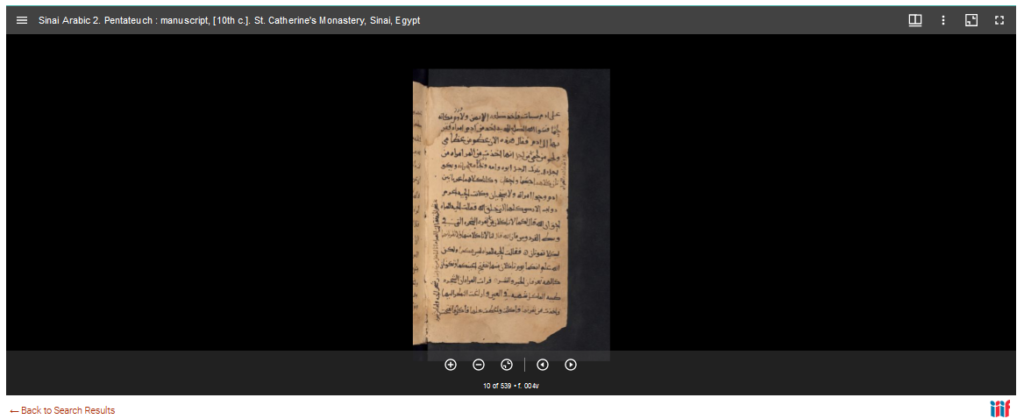
The online viewer allows to browse volumes, jump to a specific page, display a single page, double pages or a gallery. It is also possible to save pages either as image of PDF (one page at a time), share (with a permalink) or embed the image elsewhere. Unless otherwise stated, all materials are out of copyright and free of use. For more technical and legal information, you may visit this page.
bina interface is in French.