Islamic Medical Manuscripts is a project of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, the world’s largest library of the health sciences.
“The National Library of Medicine has one of the three greatest collections of Islamic medical manuscripts in the world and some of them are the only ones in existence,” says Dr. Emilie Savage-Smith.
The text for this website was written by Dr. Savage-Smith, Senior Research Associate, The Oriental Institute, University of Oxford, Pusey Lane, Oxford OX1 2LE, England. As one of the leading historians of medieval Islamic medicine, Dr. Savage-Smith has written extensively about the history of anatomy, surgery, dissection, pharmacy and ophthalmology. an American scholar from Oxford University and one of the world’s foremost authorities on Islamic medicine.
This site, with its biographies, colorful images, and extensive historical accounts of medieval medicine and science, provides students and advanced scholars an opportunity to learn about Islamic medicine and science during the Middle Ages and the important role it played in the history of Europe.

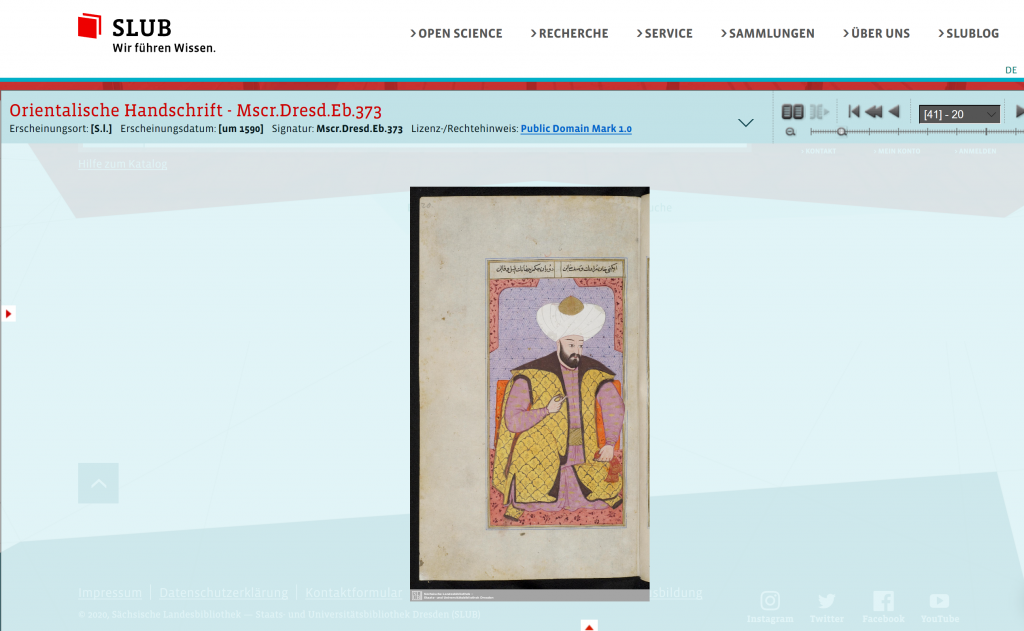
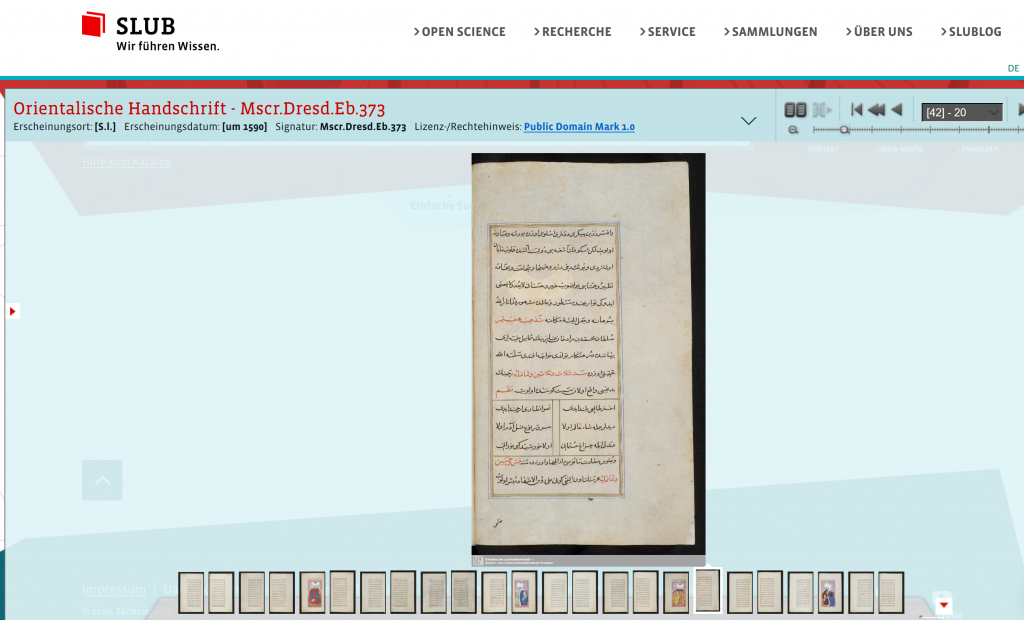
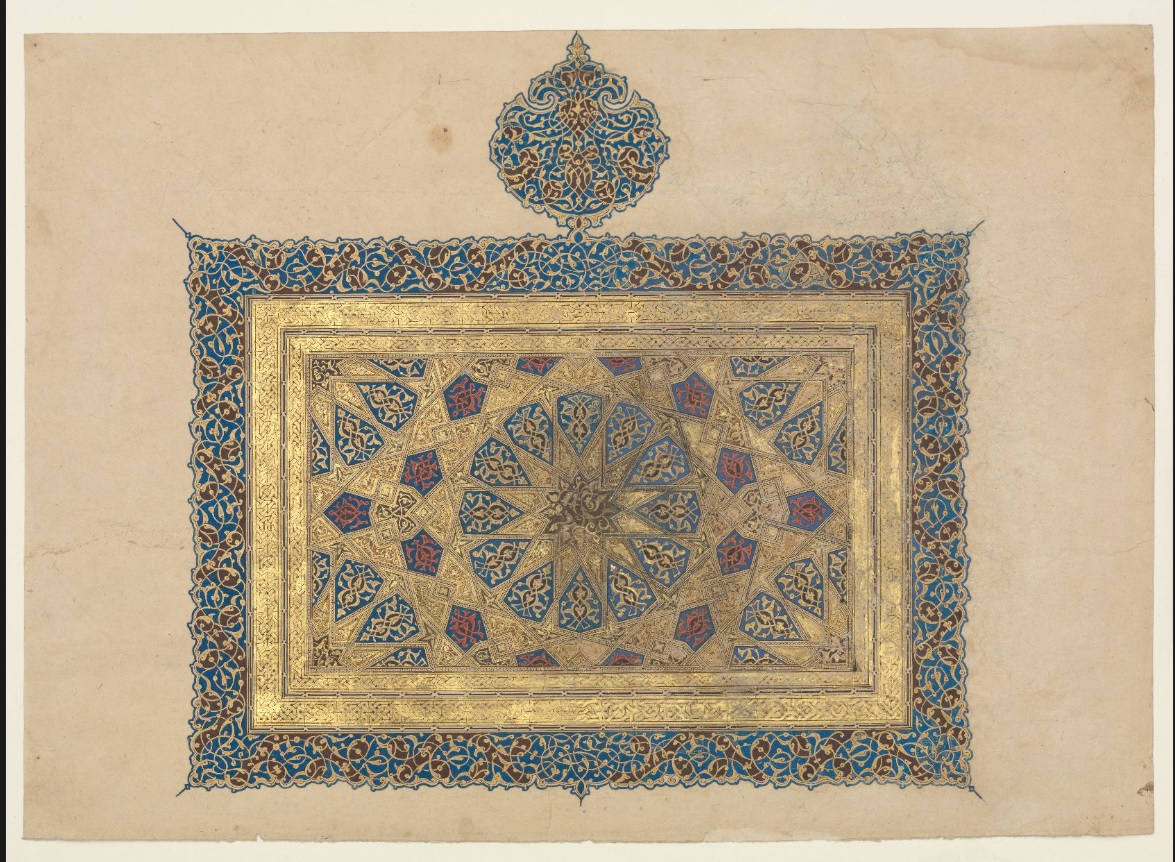
Over 300 or so Persian and Arabic manuscripts are available in the National Library of Medicine. Most of these manuscripts deal with medieval medicine and science and were written for learned physicians and scientists. Some of the manuscripts are richly illuminated and illustrated.
Where to start?
- Medieval Islam: A brief introduction to the history of Islamic medicine and and its role in European history choose
- Catalogue: To browse entries for individual manuscripts and their illustrations


- Bio-Bibliographies: To find biographies of important Islamic physicians, surgeons, and scholars, as well as suggestions for further research

- Glossary: To find out the meaning of historical terms relating to medieval medicine and book making

- Abbreviations.: To find complete bibliographical information about books and articles referred to in the entries

The Islamic achievements in this area, as well as in anatomy and surgery, led European teachers and practitioners to translate the hundreds of Arabic and Persian medical tracts into Latin and then into French, Italian, and English. In a very real sense, the European tradition of medical science and practice, which has now spread world-wide, owes a great debt to Avicenna, al-Nafis, Rhazis, Abulcasis and other Islamic practitioners and scholars.
EurekAlert! Science News Releases