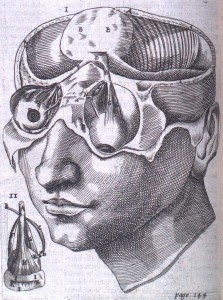
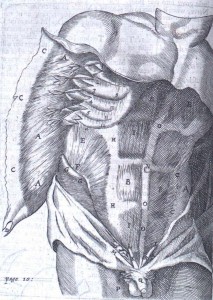
Born into a Danish family of physicians, Thomas Bartholin (1616-1680) was influenced at an early age by his relatives’ forays into anatomical science and medicine. He traveled widely throughout Europe before receiving his medical degree at Basel in 1645, and subsequently made significant contributions to 17th century anatomical knowledge, particularly concerning the discovery of the lymph vessel system as well as first recognizing the thoracic duct in humans. A prolific writer, his work was published both in Leiden and London and translated into several different languages. Like his father, Caspar Bartholin the Elder, Thomas wrote several anatomical treatises which became rather popular textbooks. This 1668 English translation of his most famous work, Bartholinus Anatomy, has recently made its way into the Osler Library. Published in London by Nicholas Culpeper and Abdiah Cole, the anatomical treatise contains 153 copperplate engravings (4 of which are fold-out plates).
The text is a later adaptation of his father’s Anatomicae Institutiones Corporis Humani (1611), which was, for many years, a standard textbook on the subject of anatomy. Caspar’s work was revised and illustrated by Thomas who published the new edition, Anatomia, in 1641. Following his observations on the human lymphatic system (along with some criticism from fellow anatomists) Bartholin updated his Anatomia, publishing a revised and augmented edition in 1655.
The younger Bartholin’s textbook differs from that of his father with the addition of references to the writings of contemporary anatomists, such as William Harvey and Gasparo Aselli. The work of these two physicians is explicitly referenced in the book’s appendix: two letters from Johannes Walaeus to the author, “Concerning the Motion of the Chyle and Blood” and “Of the Motion of the Blood.” The accompanying illustrations likewise updated the original edition. These engraved plates, roughly inserted within and often overlapping the book’s text, supplement Bartholin’s discussion of the human body. Most of these images were not original, but rather were based on the work of Vesalius, Casserio, Vesling, and other famous anatomists.
Bartholin’s Anatomy was one of the most popular anatomical texts of the 17th century. Separated into four books and four “petty books” detailing distinct sections and systems of the human body, the exhaustive work was central to the early modern study and development of the anatomical sciences.