A very important resource for the history of medicine, Morton’s Medical Bibliography (also known as “Garrison-Morton”), is now available as a database at historyofmedicine.com. Garrison-Morton is a standard reference work for the history of medicine, biology, and dentistry, originally composed of a bibliography of classic works of medicine by the American historian and librarian of medicine Fielding H. Garrison (1870-1935) in 1933. Continue reading
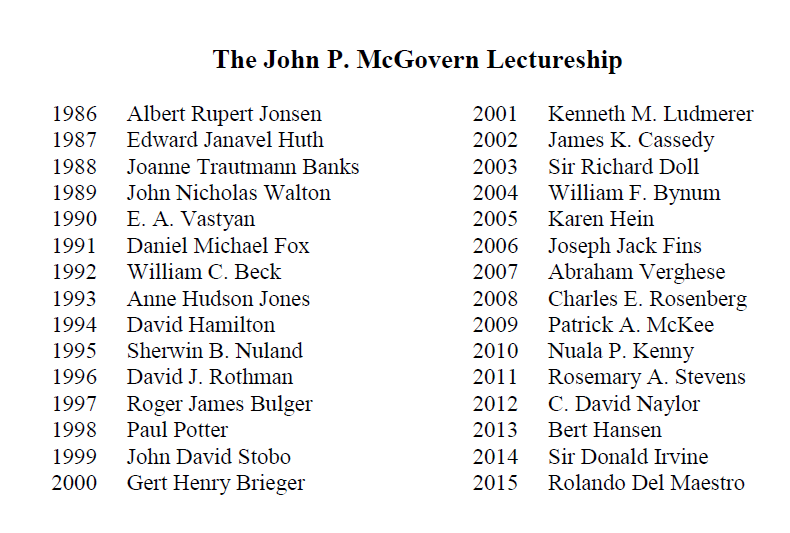
Dr. Rolando Del Maestro to Give McGovern Award Lecture
 Dr. Rolando Del Maestro, Chairperson of the Standing Committee of the Osler Library, has been honoured with the John P. McGovern Award Lectureship by the American Osler Society at the 45th Annual Meeting to be held in Baltimore from April 26 to April 29. The Lectureship was established in 1986 in honour of physician and historian of medicine Dr. John P. McGovern through the generosity of the John P. McGovern Foundation. The Lectureship is awarded yearly to a significant contributor to the field of medical humanities and the Oslerian legacy. Dr. Del Maestro is the first to receive the Lectureship from McGill University and one of only a few Canadians to be awarded the distinction. His lecture, entitled “Leonardo da Vinci and the Search for the Soul,” will be given on Monday, April 27th, and will focus on both the historical and present concepts related to neurological cognitive integration.
Dr. Rolando Del Maestro, Chairperson of the Standing Committee of the Osler Library, has been honoured with the John P. McGovern Award Lectureship by the American Osler Society at the 45th Annual Meeting to be held in Baltimore from April 26 to April 29. The Lectureship was established in 1986 in honour of physician and historian of medicine Dr. John P. McGovern through the generosity of the John P. McGovern Foundation. The Lectureship is awarded yearly to a significant contributor to the field of medical humanities and the Oslerian legacy. Dr. Del Maestro is the first to receive the Lectureship from McGill University and one of only a few Canadians to be awarded the distinction. His lecture, entitled “Leonardo da Vinci and the Search for the Soul,” will be given on Monday, April 27th, and will focus on both the historical and present concepts related to neurological cognitive integration.
Here is a list of all of the recipients of the John P. McGovern Award Lectureships since its inception in 1986:
Reprints of past John P. McGovern Award Lectures can be found in the pamphlets collection of the Osler Library. A complete listing can be found here. A collection of 18 past McGovern lectures was published in 2004 by Lawrence D. Longo: Our lords, the sick: McGovern Lectures in the history of medicine and medical humanism.
The American Osler Society was founded in the 1960s as for the purpose of bringing together members of the medical and allied professions who are, by their common inspiration, dedicated to memorialise and perpetuate the just and charitable life, the intellectual resourcefulness, and the ethical example of Sir William Osler. Since January 9, 1981, the Osler Library has been the official repository for the archives of the American Osler Society, a full description of which can be found here.
On the Surface/Skin deep: Interview with the curators
 Sylie Boisjoli and Shana Cooperstein are doctoral students in art history in the Department of Art History and Communication Studies at McGill. They are the guest curators of our current exhibition, On the Surface/Skin Deep. They agreed to answer a couple questions about the exhibition and their work.
Sylie Boisjoli and Shana Cooperstein are doctoral students in art history in the Department of Art History and Communication Studies at McGill. They are the guest curators of our current exhibition, On the Surface/Skin Deep. They agreed to answer a couple questions about the exhibition and their work.
AD: First, could you each tell me a little bit about your research interests, and current work?
SB: I’m currently working on my PhD thesis in the Department of Art History and Communication Studies and am the course supervisor for the Museum Internship class, which aims to accompany and enhance students’ internships at museums or galleries. During my MA in art history, which I also did at McGill, I conducted extensive primary research at the Osler Library for my major research paper on late nineteenth-century French artists’ visualisations of the development of serum therapy treatments against diphtheria. My PhD work has now shifted to investigate the emergence of the notion of prehistoric time in France within wider nineteenth-century scientific and philosophical debates around Darwinian evolutionary theories on the progress and mutability of the human species. By examining the social, political, and intellectual conditions in which the idea of prehistory developed, I analyze how representations of prehistoric people and places normalized the belief that time was a dynamic force that could drive forward or limit France’s progress as a nation. My work thus explores the increased public interest in representations and conceptions of prehistoric time in relation to the wider nineteenth-century impulse for reading the past and the passage of time in/on the body. My dissertation also considers the notion of prehistory as an indicator of, and participant in, a significant shift in how French society understood its national history. The fascination with prehistory was certainly not restricted to a few specialists in the human sciences. Instead, my research investigates ways in which artists, writers, and scientists disseminated their visions of the past across the French public sphere.
SC: After receiving a Master of Arts in art history at Temple University, I began pursuing a doctorate in art history at McGill University. My personal trajectory has led me to develop an interest in theories of representation, standardization, and the intersection of art and science. Bridging these areas of inquiry, my dissertation situates nineteenth-century French drawing pedagogy at the nexus of art, industrial design and the theories of knowledge. Specifically, I explore the institutionalization and reorganization of drawing in public pedagogical programs, design schools, and at the École des Beaux-Arts. In the past, I have had the opportunity to intern at various institutions, such as The Institute of Contemporary Art in Philadelphia, The Museum of Modern Art, and The Carnegie Museum of Art. I also have authored an article in Leonardo titled: “Imagery and Astronomy: The Visual Antecedents Informing Non-Reproductive Depictions of the Orion Nebula.”
AD: What led you to choose the topic of the exhibition? How did you go about exploring the topic and selecting materials?
SB: One of the most striking images in the Osler Library’s collection is the “The Flayed Angel” from an eighteenth-century medical atlas by French anatomist and printmaker Jacques Fabien Gautier D’Agoty (c.1716-1785). In this richly coloured mezzotint, a woman’s back skin is peeled away to reveal the inner anatomy of her spine and the musculature of her back. The idea of slicing and paring a portion of the body’s outer boundary led us to question how skin has been conceived as the interface between the body’s depths and surface. Although D’Agoty’s fascinating picture was at the starting point of our thinking process, eighteenth-century mezzotints and prints will (unfortunately!) have to wait for another exhibition. As specialists in nineteenth-century French art and because we knew we could display wonderful wax moulages of skin diseases from the Maude Abbott Medical Museum, we wanted to work within the scope of that century. Moreover, it’s a time when dermatology emerged as a specialized branch of medicine concerned with visualizing and diagnosing skin. Once we began to explore the vast and varied nineteenth-century materials on skin from the Osler collection, it became clear that images had played a significant role in disseminating ideas on what doctors and beauty specialists considered to be normal and healthy skin ―and thus how to diagnose skin diseases and other epidermal conditions. Indeed the authors of many of the medical texts on display in the exhibition stated that medical images were indispensable to teaching doctors how to correctly scrutinize the surface of the body. I was especially interested in why several doctors included the superficial alteration of skin pigmentation in their treatises on skin diseases. In Élie Chatelain’s Précis iconographique des maladies de la peau from 1893, the doctor provided little in the way of an explanation for the cause of vitiligo, and even less for its treatment. Yet Chatelain included a hand-painted photograph that highlights the difference between a male patient’s skin colour and patches of depleted pigment that emerged on his arms, shoulders, torso, and groin. Because of, and due to, the emphasis put on the visible aspects of skin diseases, we hope that visitors at the Osler Library will see how images were part of a medical discourse that considered changes in skin colour, for example, to be a pathological feature. By examining the medical images on display, we hope to raise larger questions about the place of medical discourse in debates about race, class, and gender in nineteenth-century society.
SC: Originally, the exhibition was scheduled to open a year ago to coincide with a guest lecture by Dr. Mechthild Fend, an art historian interested in eighteenth- and nineteenth-century representations of the body, titled “Body to Body: The Dermatological Wax Moulage as Indexical Image.” Although we were unable to move forward with the project until the Osler reopened this year, Dr. Hunter encouraged us to build from Dr. Fend’s scholarship. In doing so, we explored how art historians can profit from medical collections by analyzing depictions of skin from a humanistic perspective.
First and foremost, the availability of material at the Osler guided the scope and trajectory of the exhibition. After agreeing on the representation of epidermis in modernity as the unifying thematic of the display, I began to think about how artists depicted skin. Rather than represent individual abnormalities or eccentricities, artists historically idealized features. With this in mind, I began consulting medical atlases, scientific texts, and cosmetic handbooks with an eye toward issues of beauty and idealization, aging, and birthmarks. Tying together these themes was the ways in which abstract notions of comeliness and what constitutes comeliness shaped the representational strategies used to display “superficial” medical features. I was curious about how physicians attempted to rationalize imperfections, such as wrinkles and birthmarks, as well as how scientific “facts” lent supposedly scientific support to cosmetic “knowledge.” Likewise, I was interested in how the rationalization of imperfection often defied the well-known expression: “beauty is only skin deep.” For instance, the physiognomic study of wrinkles connected the appearance of skin to the deepest recesses of the mind.
AD: Could you describe your curatorial vision or approach to the exhibition? What have you hoped to achieve?
SB: As art historians, a consideration of how skin has been depicted in paintings that are then reproduced in beauty manuals, how skin and the diseases, blemishes, or creases that can mark it have been moulded into wax, photographed or drawn, led us to question how skin has been historically conceived. This is also why we chose to look at a diverse range of materials: treatises on hygiene, beauty manuals, as well as atlases and guides for professional medical practitioners. We believe that this allows us to explore the wider historical and social contexts in which medical knowledge on skin developed. We also hope that visitors will be able to explore the historical roots for the ongoing pressure and pursuit to have smooth and evenly pigmented skin.
SC: As previously mentioned, the broader aim of this exhibition was to convey how art historians can use medical collections. Personally, I hoped to convey the importance of interdisciplinary research to an audience with diverse backgrounds without compromising the complexity of academic scholarship. Several art historians use interdisciplinary research to highlight how other disciplines, such as medicine, shaped artistic production. I sought–and in my dissertation will continue–to do the reverse. I aim to establish how art shapes the way other disciplines have understood and continue to understand their practice. In the case of early dermatology, the most obvious manifestation of this is that physicians often hired illustrators trained in the fine arts and with particular conventions to represent case studies.
AD: What sorts of other exhibition experiences have you had or been involved in? Have you found there to be particular considerations or challenges involved in working with rare books?
SB: During my undergraduate degree in History at the University of Winnipeg I had the opportunity to intern as a curatorial assistant at the Buhler Gallery, a unique gallery located in the Saint-Boniface Hospital that aims to provide a restful and contemplative space for visitors. While interning there I helped to curate an exhibition of two Winnipeg painters, Arthur Adamson and George Swinton, entitled Marking the Message. Before starting my MA at McGill I also worked as an Art Handler Technician at the Winnipeg Art Gallery. As far as organizing and installing exhibitions, I’m used to dealing with paintings and sculptures in conventional gallery spaces. Installing the exhibition at the Osler Library presented the special challenge of how to best display the images in delicate books. On the one hand, I’m used to handling the material at the Osler Library because of extensive research on a variety of nineteenth-century topics such as serum therapy, vaccination, diphtheria, rabies, breast feeding, and theories of degeneration. For an exhibition, however, we needed to consider how to best keep the books safely open for the duration of the exhibition. This is where the expertise of the staff was a necessary part of the process (thank you Anna, Bozena, Lily, and Chris!).
SC: I have been privileged to conduct research as an intern at several museums including The Museum of Modern Art, the Institute of Contemporary Art in Philadelphia, the Carnegie Museum of Art, the University Art Gallery at the University of Pittsburgh, and at the American Jewish Museum of Pittsburgh. These experiences offered invaluable insight into the nature of curatorial research and exhibition planning, as well as how to handle art objects. Building from my work as an intern, I’ve also been privileged to curate two exhibitions at Parsons The New School for Design titled Cultural Constructs (July 15-August 1, 2013) and (Sub)contracted (July 14-July 28, 2012). Each show featured work by candidates and recent recipients of a Master of Fine Arts in photography at Tyler School of Art, Temple University. Cultural Constructs explored the representational conventions associated with cultural heritage in the contemporary moment. This show questioned the ideological assumptions determining which architectural structures, monuments, and landscapes embody or define a culture and its history. Distinct from this exhibition, (Sub)Contracted tied together the work by five artists who adopt the visual conventions associated with photography’s earliest utilitarian uses. By documenting sculptures and capturing aerial landscape photographs, for instance, their work recalls photography’s first status as a “hand-maiden” to the fine arts and sciences. Working with rare books posed new and exciting challenges for me. Because so many of the texts housed by the Osler are illustrated, the collection offers an overwhelming amount of images from which to work! Along with this, rare books pose curatorial problems in so far as they need to be exhibited in cases. Showcases qualify the physical proximity between viewers and the objects, limiting the viewer’s ability to see the images clearly. This, coupled with the fact that it was impossible to adopt exhibition practices traditionally used in art museums to highlight formal properties or details, such as changing the wall color, curators using this space are required to think creatively about how to exhibit these materials. For instance, in the section on birthmarks, the addition of a bright red cloth highlighted the intricate colors used to represent angiomas and vascular naevus. Rare books also confound the pervasive method of organizing art works chronologically in exhibitions. Because so many of the books are reprinted in different editions over the course of several years, it proved to be easiest to think about the representation of skin thematically as opposed to chronologically. Admittedly, I felt self-conscious about the curatorial process because I am a teaching assistant to a course in which students were required to examine how exhibition practices, such as the way works are organized and hung on the wall, shape the viewer’s interpretation of the show! In many respects, we tried to highlight the “look” or aesthetic of older libraries.
Thank you, Shana and Sylvie! On the Surface/Skin Deep will run through July in the Osler Library exhibition space on the 3rd floor of the McIntyre Medical Building, 3655 Promenade-Sir-William-Osler.
Archives of Dr. Charles Scriver now open

Photo from McGill’s Alumni Online Community.
An important new collection for contemporary history of medicine is now open for consultation in the McGill University Archives. The papers of Montreal pediatrician and geneticist Dr. Charles R. Scriver were donated to the Archives in 2013 and serve as a record of his 50-year career in biogenetics. His over 600 publications extend from the metabolic aspects of genetic disease in infants to bioinformatics and population genetics. Dr. Scriver’s research in the scientific community is thus situated at the nexus of genetics and pediatrics.
Dr. Scriver received his primary education at the Lower College of Canada, earned his Bachelor of Arts cum laude (1951) and M.D.C.M. (1955) at McGill’s Faculty of Medicine, and underwent clinical training at McGill and Harvard University (1955-58). From 1961 to 1966, Scriver was an appointed Markle Scholar within the Department of Pediatrics, a position which poised him to accept a full professorship of Pediatrics beginning in 1969. During this time, Dr. Scriver helped found the DeBelle Laboratory, a biochemical genetics lab under the Montreal Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Scriver’s work on vitamin D’s impact on newborn metabolic disorders (particularly rickets) during this period led to more stringent screening processes for phenylketonuria (PKU) and hypothyroidism in infants, and to the breakthrough introduction of vitamin D in Quebec grocery store milk. He is currently the Alva Professor Emeritus of Human Genetics in the McGill Faculty of Medicine and is honored in the Canadian Science and Engineering Hall of Fame.
Please contact the McGill University Archives for more information or to consult the archives.
Further reading:
George Fedak and Nam-Soo Kim. “Canadian Pioneers. Dr. Charles Robert Scriver“. Genome 51, no. 5 (May 2008): iii–iv.
Exhibit opening reception this Wednesday
2014 Osler Essay Contest Winners
The three winning essays from the 2014 round of the Osler Society and Osler Library Board of Curators Essay Contest have now been made available on our website. There was a tie for first place this year between Julian Z. Xue and Gabriel Devlin. In the essay “On Sir William Osler’s Relationship with Death,” Julian Xue (MDCM 2014) examines Osler’s personal experience of loss and argues that these encounters with death moulded his views both philosophically and practically. Gabriel Devlin (MDCM 2017) contrasts the patient-doctor relationship in North American and Southern Europe, finding that while medical paternalism was tempered in North America in the mid-20th century due to public scandals involving medical experimentation and the anti-paternalism of equal rights movements, it continues to shape doctor-patient interactions around the Mediterranean. Third place in the contest was awarded to David Benrimoh for his essay “The Zeroth Law of Medicine,” which investigates the role of physicians and the American Medical Association as an largely oppositional force in the move towards universal health care coverage in the United States. Congratulations to the winners!
The Osler Society and Osler Library Board of Curators Essay Contest was founded in 2013 to promote student research in the history, social studies, sociology, ethics, and humanities of the health sciences. Participants select a topic and are then mentored by an expert drawn from the Osler Library’s Board of Curators or elsewhere to complete their project, drawing on the rich resources of the library. The three top finalists present their essays on Osler Day in November. Prizes are awarded t of $250 for third place, $500 for second place, and $1,000 for the winning essay. The first-place winner is also awarded the Osler Library Board of Curators’ medal.
Interested in participating in this year’s contest? We are currently accepting proposals, due May 1st. Find more details here.
Announcing the Edward H. Bensley Research Travel Grant recipients
The Osler Library is pleased to announce that we have selected three researchers out of a very worthy pool of applicants to receive this year’s Dr. Edward H. Bensley Research Travel Grants to support their work at the Osler Library. This year’s recipients are Dr. Sasha Mullally, Dr. Elma Brenner, and Emily Lockhart.
Dr. Mullally is a professor of history at the University of New Brunswick. She holds a doctorate in history from the University of Toronto and is a specialist in the social history of medicine and health in Canada and the US. She is currently co-investigator on a study of the history of medical diasporas in Canada, a SSHRC- and AMS/Hannah Foundation-funded research project. Her work at the Osler Library will investigate the history of physicians immigrating to Canada in the second half of the 20th century.
Dr. Brenner works at at the Wellcome Library in London as a specialist in medieval and early modern medicine. She was previously a post-doctoral research fellow at the Pontifical Institute of Medieval Studies, where she also earned a Licence in Medieval Studies. She holds a doctorate in history from the University of Cambridge and has published on the history of leprosy in the Middle Ages. At Osler she will be looking at a number of early printed works on the “French Disease,” a disfiguring illness roughly equivalent to modern-day syphilis.
Emily Lockhart is Toronto-based photographer, designer, and curator. As a travel grant recipient, she will continue her work on a historical photographic project with McGill’s School of Architecture. The project explores the spaces of medical instruction at McGill in the wake of World War I and today by reproducing a collection of 146 glass plate negatives taken by McGill medical student James R. Lockhart (1890-1980) after the war and rephotographing the places that appear in the historic photographs as they now exist.
Congratulations to all of our 2015 recipients!
The Dr. Edward H. Bensley Research Travel Grant is endowed through generous gifts from the McGill Medicine Class of 1936 and the Pope-Jackson Fund. The grant honours Dr. E. H. Bensley’s place in the history of the Osler Library, as a former dean of the Faculty of Medicine at McGill who devoted the latter part of his life to the study of the history of medicine. For more information about the research travel grant, please see our website.
Medieval medical manuscript available digitally
The Osler Library’s copy of a medieval medical text written by Johannes de Sancto Paulo (John of Saint Paul) is one of our manuscripts that are available digitally. Bibliotheca Osleriana 7627 is a small early 13th century Latin manuscript containing the Breviarium medicine (“Breviary of medicine”) written by Johannes de Sancto Paulo (fl. 1180), as well as an excerpt from the Liber Pantegni compiled and translated from Arabic into Latin by Constantine the African (1020?-1098/99?). It was rebound probably in the late 19th century in vellum over boards with beautiful marbled pastedowns. The volume belongs to William Osler‘s original donation to the library and is catalogued in his Bibliotheca Osleriana (1). Osler acquired the manuscript from the rare books dealer Luigi Lubrano of Naples in October of 1915.

First leaf of the Breviary, with the incipit, an opening line written in red announcing the title of the text (referred to in this copy as the “Breviary of Hippocrates”) and table of contents. BO 7627.
Johannes de Sancto Paulo was a physician active in Southern Italy during the late 12th and early 13th century. He is thought to be among the masters of the Salerno school of medicine, a center for medical teaching and knowledge production well-known for bringing the work of Arabic medical writers into Europe through Latin translation. The breviary, one of four known works by Johannes de Sancto Paolo, is a general guide to practical medicine written probably around the third quarter of the 12th century.
The text is divided into five books. The first book discusses some practical issues about diagnosing and understanding disease, for example, recognizing signs of illness. It also discusses diseases that affect the entire body, like leprosy and skin conditions such as erysipelas. The second book contains conditions relating to the head and upper body, including the respiratory system. In this book are descriptions of and treatments for “psychological” conditions like mania and lethargy, head pain, eye pain, impaired vision, coughs, and asthma.

Chapter on leprosy, De Lepra from BO 7627. A popular topic, one early reader has added a lot of notes in the margin.
Book 3 concentrates on the digestive system with entries on vomiting, stomach pain, diabetes, and more. Book 4 is on the reproductive system and women’s issues like retention of menses and womb suffocation (two worrisome conditions for medieval doctors). Book 5 is on different types of fevers, which medieval people identified as a disease in itself rather than a symptom of illness, as we understand it today.
The second text bound in the manuscript appears to have been written somewhat later than the first. It was often a common practice to bind single texts together in the same binding.

A short extract from the Pantegni section on medical theory, theorica, likely transcribed by a medieval medical student. BO 7627.
The title of the manuscript’s second text, the Pantegni, comes from the Greek words pan and techne, meaning “all the art,” referring to the art of medicine, and was a large compendium of both practical medical treatments and medical theory. These pages are possibly the work of a student copying an extract of this well-known medical textbook for his own reference purposes. In the margin above where the writing begins, the scribe has scrawled in a short plea–sancti spiritus assit nobis gratia. Que cordi nostra sibi faciat, the opening (although slightly garbled) lines of a sequence hymn for the Christian holiday of Pentecost: “May the holy spirit be with us now. May he fashion to him our hearts.”
Further reading:
See a digitized copy of the oldest manuscript of the Pantegni (probably written under the supervision of Constantine himself) from the Dutch National Library here.
To find out more about medieval medicine in general, take a look at Nancy Siraisi, Medieval & early Renaissance medicine: an introduction to knowledge and practice (Chicago, 1990) or Faith Wallis, Medieval medicine: a reader (Toronto, 2010).
A great (and entertaining) resource on medieval manuscripts is the blog Medieval Fragments. A good intro to understanding and researching manuscripts is Raymond Clemens and Timothy Graham, An introduction to manuscript studies (Ithaca, NY, 2007).
References
(1) Sir William Osler, Bibliotheca Osleriana: a catalogue of books illustrating the history of medicine and science (Montreal, 1969).
(2) Monica H. Green, “Johannes de Sancto Paulo,” in Medieval science, technology, and medicine: an encyclopedia, ed. Thomas Glick, Steven J. Livesey, and Faith Wallis (New York, 2005).
Directions for Preserving Health in St. Louis, 1874

“Dr. C. H. Sanborn’s Directions for Preserving Health in St. Louis, 1874.” Osler Library Archives, P192
The Osler Library recently acquired a short manuscript booklet containing one doctor’s medical advice for patients moving out of town. Labelled “Dr. C. H. Sanborn’s directions for preserving health in St. Louis, 1874,” this tiny treatise provides advice and recipes for treating day-to-day complaints and guidelines for stocking the family medicine cabinet with the essentials.
Dr Charles H. Sanborn was a physician practicing in New Hampshire. Born in Hampton Falls in 1822, he graduated with an MD from Harvard Medical School in 1856 (1). He practiced medicine for over forty years in his hometown, where he also served as a Justice of the Peace and in local government (2). This autograph booklet appears to have been written by him for a family of three moving from New Hampshire to St. Louis, Missouri.

“The Pictorial Guide to St. Louis,” 1877. From the Internet Archive.
During the second half of the 19th century, St. Louis was undergoing a population explosion that would make it the fourth largest city in the U.S. after New York, Philadelphia, and Chicago. Expanding sectors, such as the cotton industry, and new railroad connections attracted an influx of new residents, perhaps including Dr. Sanborn’s patients. The city was prone to cholera and had lived through an epidemic that killed more than 3,500 residents in 1866, just eight years prior to the writing of Dr. Sanborn’s pamphlet. (3)
Fittingly, Dr. Sanborn’s medical advice concentrates heavily on cholera and other, less acute gastro-intestinal complaints associated with moving to new climes. The first page of medical instructions deals with how to treat “Diarrhea, Dysentery or Cholera Morbus” in the youngest member of the family. Remedies include starch, castor oil, bismuth, and, in the case of feverishness, veratrum viride, a highly toxic plant sometimes used during the 19th century in the treatment of typhoid fever and yellow fever.
Up until the late 19th and early 20th century, the majority of medical treatment took place at home. Popular printed medical manuals would have been readily available for purchase and families would have expected to care for their sick themselves:
The skills, knowledge, and responsibilities of laypersons and physicians overlapped; trained physicians were in a functional sense always consultants–with the primary caregiver a family member, neighbor, or midwife.(4)
In the case of Dr. Sanborn’s patients, the father was perhaps the one responsible for making medical decisions and treating his family. Advice for particular ailments is oftentimes labelled “Baby” or “Self & Wife,” and includes detailed instructions for treating croup, “lung fever,” measles, the “Shakes,” “weakness sinking etc. etc.,” sore throat, painful menstruation, inflamed eyes, burns, and bug bites. A list in the back of the book ennumerates the items that should be kept on hand for medical usage.
 One of the chemicals on this list attests to the persistence of the miasma theory of disease into the second half of the 19th century, even as germ theory was beginning to emerge in scientific circles around the same time. Disease, it was thought, was transmittable by poisoned air, marked by a bad smell. Dr. Sanborn suggests the use of bromo-chloralum, a harsh disinfectant, to “destroy most every poison in the atmosphere.” He urges it to be used liberally in the baby’s room and all around the house: “Don’t fail to use a pound of two in the first month or two.”
One of the chemicals on this list attests to the persistence of the miasma theory of disease into the second half of the 19th century, even as germ theory was beginning to emerge in scientific circles around the same time. Disease, it was thought, was transmittable by poisoned air, marked by a bad smell. Dr. Sanborn suggests the use of bromo-chloralum, a harsh disinfectant, to “destroy most every poison in the atmosphere.” He urges it to be used liberally in the baby’s room and all around the house: “Don’t fail to use a pound of two in the first month or two.”
______________________________
This pamphlet is now available for consultation in our archives. You can find it listed on the Osler Library Archives database. For more information, please contact the library.
Further reading:
W. F. Bynum, Science and the Practice of Medicine in the Nineteenth Century. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994.
William G. Rothstein, American Physicians in the Nineteenth Century: From Sects to Science. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1972.
Charles E. Rosenberg. Our Present Complaint: American Medicine, Then and Now. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
Charles E. Rosenberg, ed. Right Living: An Anglo-American Tradition of Self-Help Medicine and Hygiene. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992.
References
(1) Harvard University. Quinquennial catalogue of the officers and graduates, 1636-1930. (Cambridge, MA, 1930).
(2) Warren Brown, History of the Town of Hampton Falls, New Hampshire from the Time of the First Settlement within its Borders, vol. 1 (Manchester, NH, 1900.); The New Hampshire Register, Farmer’s Almanac, and Business Registry for 1871 (Claremont, NH, 1871).
(3) History of St. Louis, (1866-1904) http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=History_of_St._Louis_(1866%E2%80%931904)&oldid=638231408
(4) Charles Rosenberg, ed. Right Living: An Anglo-American Tradition of Self-Help Medicine and Hygiene. (Cambridge, 1992), 4.
Reminder: March 1st deadline for Osler research travel awards
Please note that the Osler Library is accepting applications until March 1st, 2015 for the Mary Louise Nickerson Fellowship (up to 10,000$) and the Dr. Dimitrije Pivnicki Award (up to 4,000$). Both are directed towards researchers working in the field of neuro history to enable them to travel to Montreal to use the extensive resources of the Osler Library (including the Wilder Penfield Archive), as well as those of the McGill University Archives and the Montreal Neurological Institute.
Please follow the links above for information on how to apply.