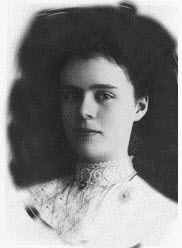 Annie Langstaff, née MacDonald, a legal author, feminist, and aviatrix, was the first woman graduate in law in Québec (first-class honours, 1914), who became known because of her litigation against the Québec Bar, where she was denied access to its qualifying exams. To honour her memory the Law Library opens an exhibition featuring a selection of archival materials, including her original diploma, photographs, and grades’ transcripts.
Annie Langstaff, née MacDonald, a legal author, feminist, and aviatrix, was the first woman graduate in law in Québec (first-class honours, 1914), who became known because of her litigation against the Québec Bar, where she was denied access to its qualifying exams. To honour her memory the Law Library opens an exhibition featuring a selection of archival materials, including her original diploma, photographs, and grades’ transcripts.
She was born in 1887 in Alexandria, Glengarry County, Ontario. She came to Montreal, after receiving her Senior Matriculation from the Prescott (Ontario) High School, and worked as a stenographer for Samuel W. Jacobs, K.C., head of the firm Jacobs, Hall, Couture and Fitch, a well-respected lawyer and advocate of Jewish Rights.
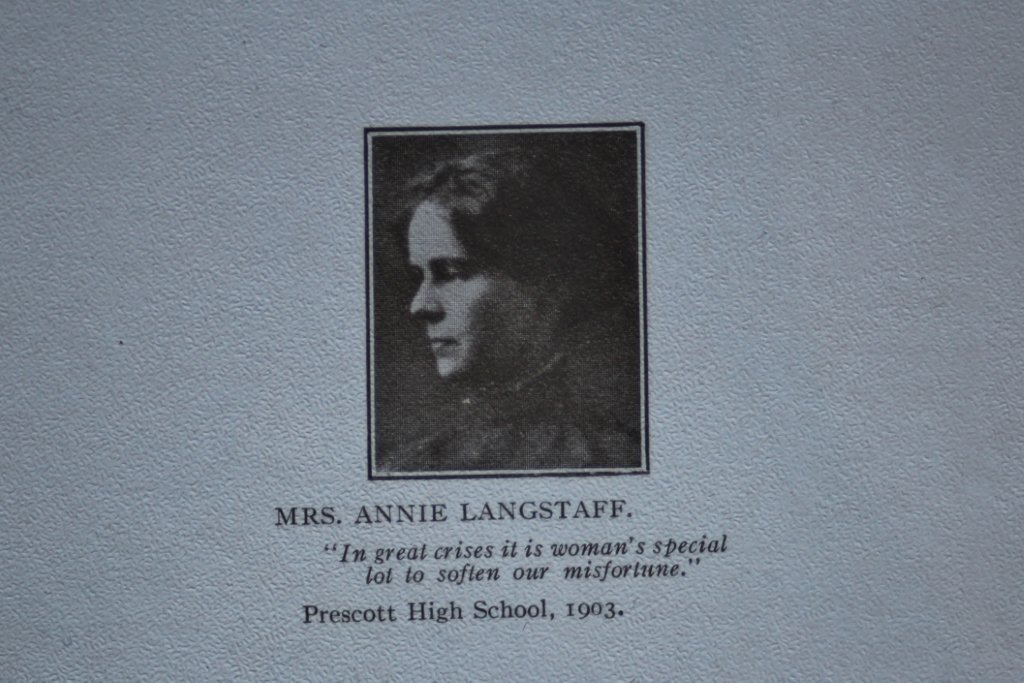
 In October 1911, with the encouragement of Mr. Jacobs, she entered the McGill Faculty of Law. She received her B.C.L. in May 1915, graduating with First Class Honours and a prize of $25.00. She ranked fourth in her class of eighteen and led her second year class in Company Law and her third year class in Criminal Law. After Convocation she applied to take the Quebec preliminary Bar examination. This examination was normally taken, by those wishing to study law, three years before presenting themselves for admission to practice and as a preliminary to the university program in law. Mrs. Langstaff, anticipating difficulty in being admitted, chose to complete her law program first, and then to apply for the preliminary examination.
In October 1911, with the encouragement of Mr. Jacobs, she entered the McGill Faculty of Law. She received her B.C.L. in May 1915, graduating with First Class Honours and a prize of $25.00. She ranked fourth in her class of eighteen and led her second year class in Company Law and her third year class in Criminal Law. After Convocation she applied to take the Quebec preliminary Bar examination. This examination was normally taken, by those wishing to study law, three years before presenting themselves for admission to practice and as a preliminary to the university program in law. Mrs. Langstaff, anticipating difficulty in being admitted, chose to complete her law program first, and then to apply for the preliminary examination.
Her application was refused by the Bar and, with Mr. Jacobs as her counsellor, she petitioned the Superior Court for a writ of mandamus summoning the Quebec Bar to show cause why it should not be ordered to grant the application since Mrs. Langstaff met all the statutory qualifications for sitting the examination. At the hearing, Mrs. Langstaff assisted in the presentation of her case. Her petition was dismissed with costs by Mr. Justice Saint-Pierre. (Dame Langstaff v. The Bar of the Province of Quebec (1915) 47 C.S. 131.).
Mr. Justice Saint-Pierre noted that Mrs. Langstaff was “a young woman of good morals and possessed of considerable ability” (p. 145), but his Lordship held that “to admit a woman and more particularly a married woman as a barrister as a person who pleads cases at the bar before judges or juries in open court and in the presence of the public, would be nothing short of a direct infringement upon public order and a manifest violation the law of good morals and public decency” (p. 39). The opinion of Mr. Justice Saint-Pierre caused a public outcry. It was the subject of a number of newspaper headlines and articles. Mrs. Langstaff’s supporters, led by Professor Carrie Derick of McGill, and the members of the Local Council of Women, organized a mass protest against his remarks and decision.
Mrs. Langstaff, still represented by Mr. Jacobs, appealed to the Court of King’s Bench. A hearing was held on 16 September 1915 and arguments were closely covered in the local press. On 2nd November, the Court in a four to one decision (Mr. Justice Lavergne dissenting), affirmed Mr. Justice Saint-Pierre’s decision (Dame Langstaff (Annie Macdonald) v. The Bar of the Province of Quebec (1916) 25 B.R. 11.). Although that was the end of her personal legal battle, she continued to fight by supporting various bills introduced to change Quebec law so as to allow women to practise law.  But she was never allowed to write the examination and by the time the law was finally changed, in 1942, a Bachelor of Arts degree had become a prerequisite. Mrs. Langstaff was not prepared at the time in her life to return to formal university studies. Mrs. Langstaff continued her work for the law firm (which she described as “a little secretarial work, a little bookkeeping, and a little law”, McGill Reporter, 11 February 1976).
But she was never allowed to write the examination and by the time the law was finally changed, in 1942, a Bachelor of Arts degree had become a prerequisite. Mrs. Langstaff was not prepared at the time in her life to return to formal university studies. Mrs. Langstaff continued her work for the law firm (which she described as “a little secretarial work, a little bookkeeping, and a little law”, McGill Reporter, 11 February 1976).
She was the first woman stenographer employed in a Montreal Criminal Court (Court of Special Sessions, June 1914). She became a successful aviatrix and, on the occasion of Marshall Foch’s visit to Montreal, circled above the city for an hour to the delight of thousands of spectators. She was the author of several articles on family law published in popular women’s journals and of an English-French French-English Quebec Legal Dictionary (1937). She retired from the firm, now known as Phillips and Vineberg, in 1965 at the age of 78. She died on 29 June 1975 at the age of 88.
On September 7, 2006 The Montréal Bar bestowed on Mrs. Annie MacDonald Langstaff a posthumous honour by giving her the Medaille du Barreau de Montréal in recognition of her accomplishments.
Information and text for this blog post were derived from the memorial plaque exhibited in the Annie Langstaff room at the Faculty of Law, McGill University.

